* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to PSpice
Topology (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Ringing artifacts wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to PSpice
Syafeeza Binti Ahmad Radzi
Computer Engineering
Department
FKEKK
Review
Multisim – Digital circuit
PSpice – Analogue circuit (electric /
electronic circuit)
PSpice
Same function as Multisim
Can be used to design
- Digital circuit
- Analogue circuit
- PCB design
- IC design
Multisim is used for education purposes while
PSpice is widely used in the industry.
What Can You do with PSpice
DC Node Analysis
LAB 5
DC sweeps, component value sweeps
Small signal parameters
Frequency response & Bode Plots
Transient Response
Temperature analysis
Monte Carlo Analysis (for component variations)
Noise Analysis
4.0 DC NODAL ANALYSIS
Every analysis begins with DC Node
calculation.
Calculate only DC currents and voltages.
Capacitors open circuits.
Circuit inductors short circuits.
4.1 BASIC DC NODAL
ANALYSIS
DC NODAL ANALYSIS
Create Netlist: Analysis Create Netlist.
Simulate the circuit: Analysis Simulate.
We will see that the IPROBE and VIEWPOINT parts display the
results of the node voltage analysis.
The results of analysis are kept in the output file.
Examine the netlist file: Analysis Examine Netlist.
(shows the circuit connection and the number of node)
Examine the output file: Analysis Examine Output.
(shows the result of the node voltage analysis)
4.1 BASIC DC NODAL ANALYSIS
VIEWPOINT
IPROBE
The IPROBE and VIEWPOINT parts can be used to display the results of the
Nodal Analysis On The Schematic.
Or you can click the V and I button to display the voltage and current.
5.0 DC SWEEP ANALYSIS
To find all DC voltages and currents of a
circuit.
The DC Sweep is similar to the node
voltage analysis, but adds more flexibility.
If we use the DC Sweep, we can simulate
the circuit for several different values of
voltage / current source in the same
simulation.
5.1 BASIC DC SWEEP ANALYSIS
How does Vo vary as V1 is raised from 0 to 25 volts?
DC SWEEP
PROBE: Trace Add.
Click V(Vo) : voltage at the node Vo vs V1.
We can also display current through any device of the circuit vs V1.
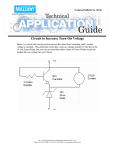
5.3 MAXIMUM POWER
TRANSFER
Objective: To analyze what value of Rs in
the circuit that will deliver maximum power
to RL.
Max Power Theorem: Max power occurs
when RL = Rs
Adding parameters
Change RL value to {RL_val}
N.B. name is unimportant but {
} are mandatory
Add a PARAM symbol
(Draw/Get New Part…/ Param)
Set up NAME1 and VALUE1
PARAM values (double-click
on the symbol).
Click OK
Set-up Parametric sweep
Setup a Parametric
sweep
(Analysis/Setup…/
DC Sweep)
Click OK
Run DC sweep analysis
Example: MAXIMUM
POWER TRANSFER
power absorbed by RL:
V(VL)*V(VL)/RL_val vs
RL
P=V2/R
RESULT
Max power transfer
occurs when
RL_val=1kohm
Result: Max power transfer occurs when RL_val = 1kohm
Kirchoff’s Law
Kirchoff’s Current Law = The algebraic
sum of the currents entering a node is
zero
I
1
I3
I2
I1 + I2 = I3
I1 + I2 – I3 = 0
Cont.
Kirchoff’s Voltage Law = The algebraic sum
of the voltages around a closed path is zero.
V1 = VR1 +VR2 +VR3
V1 – VR1 – VR2 – VR3 = 0
6.1 TASK 1: DC NODAL
ANALYSIS
Loop 2
I3
1k(I2 - I1) + 2kI2 = -12
1kI2 – 1kI1 + 2kI2 = -12
II1
1
I2
-1kI1 + 3kI2 = -12 ---(2)
Loop 1
Loop 3
3k (I1 - I3) + 1k(I1 – I2) = 12
3k(I3 - I1) + 2kI3 =12
3k I1 – 3kI3 + 1kI1 – 1kI2 = 12
3kI3 – 3kI1 + 2kI3 =12
4kI1 – 1kI2 – 3kI3 = 12 ---(1)
-3kI1 + 5kI3 = 12 ---(3)
Cont.
Solve the equation using Cramer’s Rule.
Find the value of I1, I2 and I3. Then, find
the DC node voltages for the circuit.
Ax = b
4k -1k -3k
I1
-1k 3k
0
I2
-3k
5k
I3
0
12
=
-12
12
PSPICE: AC ANALYSIS
AC Sweep:
To find Magnitude and Phase of voltage and
currents
plots magnitude versus frequency
plots phase versus frequency.
Analysis: Bode Plots, gain and phase plots,
and phasor analysis.
Applications: To see the frequency response
of an amplifier and a filter.
Source: Vac or Iac.
BODE PLOTS
Magnitude vs Frequency
Bode Plots Frequency Response
Phase vs Frequency
Passive Filter (has R,L,C components)
Filter
Active Filter (has active components e.g: BJT) normally
operates as an amplifier.
Types of filter:
1. Low Pass Filter
2. High Pass Filter
3. Band Pass Filter
4. Band Stop Filter
AC Analysis versus Transient Analysis
Source
AC SWEEP
TRANSIENT
ANALYSIS
VAC/IAC
VSIN/ISIN/pulse etc
(time-varying sources)
Analysis Magnitude vs. frequency
Phase vs. frequency
(Bode Plot)
Setup
Set point/dec;
Start frequency, End
Frequency
Voltage vs. time
Current vs. time
(Waveform vs. time)
Set final time; print
step
Set-up VAC source
Set-up VAC*
DC=0
used to find initial DC
solution
ACMAG=1
source p-to-p value
during AC analysis
ACPHASE=0
reference for phase
measurements
Set-up AC analysis and Probe
From Menu
Analysis/Setup…
or Toolbar Click “AC Sweep”
Enter as shown
Click “OK”
Application:
Measure the f3dB point of v_out using the cursors
In Probe:
Trace/Add, DB(V(v_out))
To make cursors active select
Place one cursor on
nominal 0dB point
Move other cursor until “dif”
shows difference of 3dB
Measure the f3dB point of v_out using a goal
function
In Probe:
Trace/Eval Goal Function…
Select:
LPBW(1,db_level)
Select:
V(v_out)
Enter 3 from the keyboard
Click on OK
N.B. to see a detailed explanation of this goal function and its parameters,
select:
Trace/Goal Functions, LPBW, View
The g.f. can also be evaluated from this window (select Eval instead of View)
Filter Design (3dB cutoff) – Example:
Low Pass Filter
Amplifier Gain Analysis
A=Vo/Vin
Vin=1V
A=Vo
Gain=20 * log10 A
Gain = 45.7 dB
Lower 3dB Freq=62.1 Hz
Upper 3dB Freq=6.9 MHz
Use calculations to prove this
simulations!
Transient Analysis
Waveform (voltages or currents) versus time.
Pspice will simulate the time response of the
circuit.
Sources: Vsin, Isin, Vpulse, Ipulse, etc.
The duration of simulation depends on the time
constants in the circuit.
Specify the step size, or time increment, to be
used by Pspice.
Use probe to view the results graphically. Probe
will generate plots of voltage or current versus
time.
Transient Analysis Setup
Transient Analysis Setup:
Final Time:
Final Time is the length of simulation.
F VSIN = 60 Hz
T = 1/F = 1/60 s
For 3 cycles simulation:
3T = 3 (1/60)
= 50 ms = FINALTIME
Print Step:
Every Print Step seconds, the probe
will print out the specified values in
the output.
Choose Print Step = 1ms
No Print Delay:
If we want to print data for the last
20ms of simulation:
No-Print Delay = 50ms – 20ms
= 30ms
PSpice will save and print simulation
data after this time.
Step Ceiling:
Leave it blank to get the fastest
simulation time.
PSpice will take the largest value of
Step Ceiling allowed for simulation, but
the plot maybe jagged.
Reduce Step Ceiling to obtain
smoother and nicer plot by divide with
some numbers of points.It will increase
simulation time.
Step Ceiling= T/1000 points
= (1/60) / 1000
= 0.01667ms
Example: Amplifier Voltage Swing
Monte Carlo Analysis
INTRODUCTION:
To assign tolerance values of components.
Example: Resistors have values indicated in color code
– and they never change.
In the real world, all resistors have tolerances, which
specify how they might vary from their nominal values.
To determine the effects of such tolerance variations,
PSpice offers Monte Carlo Analysis.
MONTE CARLO
Used to observe how device tolerances
can effect a design.
2 types of Analysis:
Worst Case: to find maximum and minimum
value of parameter given tolerances.
Monte Carlo: to estimate tolerance variation.
Device Model:
Uniform Distribution
Gaussian Distribution
MODEL: Tolerance - Distribution
Resistor:
.MODEL R5pcnt RES(R=1 DEV/UNIFORM 5%)
.MODEL R5gauss RES(R=1 DEV/GAUSS 1.25%)
NPN BJT Transistor:
.MODEL QBf NPN(Bf=200 DEV/UNIFORM 150)
.MODEL Q2N3904B NPN(Is=6.734f DEV/UNIFORM 10%
Xti=3 Eg=1.11)
Capacitor:
.MODEL CAP20_80 CAP(C=1.3 DEV/UNIFORM
38.461538%)
Example:Voltage divider
Using 5% resistor with
Gaussian distribution. Find
gain, Av=Vo/Vin
By calculations:
1) Nominal voltage gain.
2) Worst case maximum gain.
3) Worst case minimum gain.
By analysis – worst case
analysis.
Worst case analysis setup and
output file
Monte Carlo
To estimate % tolerance variation that pass
specifications-in case max and min value
exceed specifications.
Monte Carlo output file
f=lV(Vo)-0.5l
Gain=(Nominal gain)(deviation)
=(0.5)-(0.0202)
=0.4798
% of nominal =
[0.5/0.4798]*100
=104.03% upper
Pass>0.01 [0.5-0.49=0.01]
Monte Carlo – Probe as histogram
histogram
Uniform Distribution
Sigma
0.0102217
Minimum
0.475392
Maximum
0.524402