* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ECE 353 Lesson Slides
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Microprocessor wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Direct memory access wikipedia , lookup
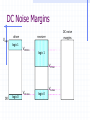
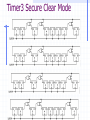
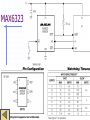
ECE 353 Introduction to Microprocessor Systems Week 8 Michael G. Morrow, P.E. Topics Logic Compatibility Microprocessor peripherals Timers Periodic Watchdog Real-time ADuC7026 timers Pulse-width modulators (PWM) Direct memory access (DMA) FET Basics Field effect transistors (FETs) are used as the switching elements in logic gates When turned on, the FET presents a very low impedance to current, like a closed switch When turned off, the FET presents a very high impedance to current, like an open switch There are two ways to construct a FET N-channel P-channel Logic Outputs Totem-pole Three-state (tri-state) Open-drain Logic Family Characteristics Voltage VIHmin – minimum input voltage recognized as a logical 1 VILmax – maximum input voltage recognized as a logical 0 VOHmin – minimum voltage output for a logical 1 VOLmax – maximum voltage output for a logical 0 Current Currents are defined positive in, negative out IOHmax – maximum output current sourced for a logical 1 IOLmax – maximum output current sunk for a logical 0 IIHmax – maximum input current required at a logical 1 IILmax – maximum input current required at a logical 0 IOZH, IOZL – current drawn/sourced when tri-stated Logic families Simple Circuit Models Drivers Receivers DC Noise Margins Vlogic driver DC noise margins receiver logic 1 VOHmin logic 1 VIHmin 0V logic 0 VOLmax VILmax logic 0 Logic Compatibility Static (DC) Compatibility Voltage Current Overvoltage tolerant inputs Dynamic compatibility Capacitive loading, mutual induction, reflections, etc. Exercises Timer Peripherals Timer/counter modules used to Generate signals with specified frequency / duty cycle Count external events, measure pulse width Generate absolute delays, periodic interrupts Building a timer peripheral Basic free-running timer Periodic timer enhancements Clock selection and prescaling Adding capture capability A Basic Free-Running Timer A Periodic Timer Clock Selection and Prescaling Capture Capability Real-Time Clocks (RTCs) RTCs provide microprocessor systems with absolute time information Absolute time does not necessarily mean calendar/clock time Typically operate from 32.768KHz crystal with battery or capacitor back-up power supply Generate periodic interrupts Often contain a small amount of RAM – historically this was where the PC stored its configuration (BIOS) settings since it was non-volatile. Dallas Semiconductor DS1375 Watchdog Timers Watchdog timers are used to guard a system against lock-up due to software errors or soft failures in hardware Often included in microcontrollers and CPU supervisor circuits. Retriggering is usually done in the main program loop Watchdog output can be used to reset the CPU or as a nonmaskable interrupt (NMI) Maxim MAX6323/MAX6324 ADuC7026 Timers Timer0 A basic periodic timer, intended to be used as the RTOS timer 16-bit counter, free-running or period register CPU core clock with prescaler Generates interrupt and/or ADC conversion trigger MMRs ADuC7026 Timers Timer1 General-purpose timer 32-bit counter Multiple clock sources with prescaler Capture register Binary or H:M:S formats ADuC7026 Timers Timer2 Wake-up timer 32-bit counter Can run on 32kHz clocks Binary or H:M:S format ADuC7026 Timers Timer3 Watchdog or generalpurpose timer 16-bit counter 32kHz clock source Watchdog timer is reset by writing to T3CLRI MMR Requires pseudo-random sequence in secure clear mode Timer3 Secure Clear Mode PWM Peripherals A basic pulse-width modulator peripheral creates a rectangular wave whose duty cycle can be controlled PWM allows us to control the average power delivered to a load without changing the voltage supplied to it The ADuC7026 contains a very capable 3-phase PWM that is intended to do motor control DMA Controllers Direct memory access (DMA) controllers are peripherals devices designed to offload data movement from the processor A common use is in servicing peripherals by collecting a frame of data for the CPU to work on, or sending out a frame of data to a peripheral as it needs it To use DMA, we need to Program the DMA controller for the task Processor does other things The DMA controller interrupts the processor when it has completed. DMA controllers usually have an auto-reload feature to do a repetitive task without the CPU having to reconfigure it every time. DMA Controllers (cont) Typical DMA controllers are programmed with the following information Source address and destination address Should address be modified at each transfer, and by how much? Transfer size How many bytes should it transfer each time? Number of transfers Trigger event What causes the DMA controller to do transfers? Wrapping Up Homework #4 is due Wednesday, March 21 Reading for next week Textbook 11 ADUC 9-10, 33-36, 43-47, 79-82 Logic Compatibility Exercises For the following logic families, determine compatibility, noise margins, and fan-out. 74ALS driving 74AC 74AC driving 74ALS VOHmin VIHmin VOLmax VILmax IOHmax IIHmax IOLmax IILmax 74ALS 2.7V 2.0V 0.5V 0.8V -400uA +20uA +8.0mA -200uA 74AC 0.7*VCC 0.1V 0.7V 0.3*VCC -50uA -24mA +1uA +50uA +24mA 4.9V 3.76V Note: For 74AC, top line is with CMOS load, bottom line is with TTL load. -1uA TinyLogic and Little Logic TM Timer0 MMRs T0LD – load counter value T0VAL – read counter value T0CLRI – clear timer interrupt T0CON - Configuration DS1375 RTC MAX6323 PWM DAC Use PWM digital output driver LPF removes most of AC components VPWM VOUT VPWM VOUT VAVERAGE Vout Vavg 1 an cos( 2ft * n) bn sin( 2ft * n)