* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electric Potential Difference Or Voltage
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
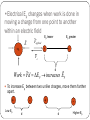
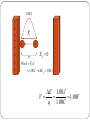
Electric Potential Difference Or Voltage Forces and Fields 8 Consider a mass positioned in a gravitational field Work EP W Fapp d W 9.81N (3.00m) 29.4 J E p mgh 3.00m 1.0kg E p 19.6 J 2.00m Fg Fup A mass above a reference level (ground) possesses gravitational potential energy. Work must be done against the force of gravity to increase Ep. (Lifting the object further off the ground increases Ep) Between the two points in the gravitational field above the ground,(2m and 5m) the difference in Ep can be determined. Consider a charge placed within an electric field Electric Potential Energy Work E p Fdown E p greater - E p d E p lesser - Fup Fe Fe - E p lesser E p d - E E p greater E + charge - charge • moving the – charge away from the positive charge requires work which increases electric potential energy and moving the – charge toward the negative charge also does the same •Electrical Ep changes when work is done in moving a charge from one point to another within an electric field Fapplied E -q1 Ep lesser Ep greater + + Fe d Work Fd E p increases E p To increase Ep between two unlike charges, move them farther apart. + Low Ep d + d Higher Ep •To increase electric Ep between two like charges, move them closer together d + d + Low Ep + + Higher Ep Electrical Potential Difference or Voltage (V) the ratio of the change in energy (work, potential or kinetic) per unit charge (1.00 C) within an electrical field Eg) two oppositely charged plates E - uniform - + + + + High Ep low Ep + + - + - + - + E p + - Between the two points that a positive charge has moved within the electric field, there exists a voltage Electric potential difference or voltage is the change in potential energy per unit charge. Equation: In Joules E V In Coulombs q units are in J / C which is equivalent to volts The ratio of E/q is called a volt and is named after Alex Volta who invented the battery Examples: A 12.0 volt battery supplies 12.0 joules of energy to move a 1.00 C charge through a circuit. The voltage of 1.00 V between two points in an electric field means that 1.00 J of energy is needed to move a 1.00 C charge between the two points in the field. 1.00 V + - + - + + + Fe - + - Ek 0 + + - Work Fe d - - 1.00 J E p 1.00 J - E 1.00 J V 1.00V q 1.00C Example: A charge of -2.60 X 10-3uC is moved from a positive plate to a negative plate by doing 1.17 X 10-5 J of work. What is the potential difference between the plates? W 1.17 105 J + - + - q 2.60 109 C - V + + + Fe - - - + + + - - Fapplied - E V q 1.17 105 J 2.60 109 C 3 4.50 10 V 2nd Equation for Voltage The potential difference or voltage between two oppositely charged plates is determined by the magnitude of the uniform electric field, E, and the distance between the plates. Equation for voltage between oppositely charged plates: E V q Work, Ep or Ek, energy Fe W Fe d but E and Fe Eq q So W Eqd Eqd So V q V V Ed and E d Example: Determine the electric field strength between 2 oppositely charged plates 25 cm apart to which 120 V is supplied. 0.25 m - + + + + E - + - + - + - + V = 120 v V Ed V E d 120V E 0.250m 480 V / m