* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Boost Converter
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
HVDC converter wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
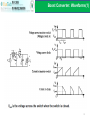
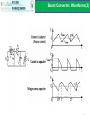
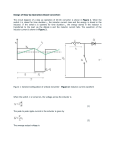
升壓式轉換器 Boost Converter Instructor: Po-Yu Kuo (郭柏佑) 國立雲林科技大學 電子工程系 Boost Converter A boost converter is shown below. It is called a boost converter because the output voltage is higher than the input When the switch is ON, inductor current increases. When the switch is OFF, inductor current decreases and charges up the capacitor. In that time, voltage at node A must be greater than Vs for decreasing the inductor current. Assume voltage across the diode is zero, Vo > Vs 2 Boost Converter: Steady-State Analysis (1) 3 Boost Converter: Steady-State Analysis (2) If the switch is open and D is zero, the output is the same as the input. As D increases, the denominator becomes smaller and the output becomes larger than the input. i.e. the boost converter can only produce an output voltage higher than or equal to the input voltage As D approaches to 1, the output voltage goes to infinity according to the equation. However, it is not the case for non-ideal components and this will be discussed later An alternative derivation using volt-second balance equation(conservation of flux in inductor): average inductor voltage is zero for periodic operation. i.e. 4 Boost Converter: Inductor Value(1) Now the inductor current IL is not the same as the load current. In fact, IL is the source current Is. Since the input power equals to the output power, Ps = VsIs = VsIL and Po = Vo2/R, the inductor current can be computed as The maximum & minimum inductor current can be computed as 5 Boost Converter: Inductor Value(2) Since the inductor current is always positive (CCM). To satisfy ILmin must be greater than 0 The minimum inductance value required for CCM operation is 6 Boost Converter: Output Voltage Ripple Similar to the buck converter, the output voltage cannot be kept perfectly constant with a finite capacitor value. The ripple voltage vr can be computed as follow When the switch is closed, the capacitor is discharged by the load current: The change in capacitor charge can be calculated from The ripple voltage is given as It should be noted that fs >> 1/RC where RC is the time constant of the output 7 Boost Converter: Waveforms(1) 8 Boost Converter: Waveforms(2) 9