* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Phisiology (L04) Slide#86: back to slides 66,67 and 68 for more
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
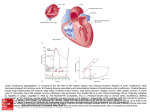
Phisiology (L04) Slide#86: back to slides 66,67 and 68 for more details. -This is the ECG. -There is the delay: which gives a chance to left ventricle to be filled with blood again. -Delay after QRS: is where the heart actually contracts = ST segment = Plateau. Slide#87: -Relaxation of the heart = diastole. -Remember: pressure difference is the force of blood movement. - The ventricle is filling with blood, right toward the end of this, the atrium contracts ; we have systole and after systole, the AV valve closes. Slide#88: -Isovolumic contraction is the beginning phase of ventricular systole. -The pressure in ventricles is increasing due to closing of AV valves, (in left side, due to closing of mitral valve, the left ventricle starts to compress and compress , until the pressure in ventricle increases and the aortic valve opens). Slide#89: -After opening of aortic valve, the left ventricle pushes its containing of blood to aorta and then the aortic valve closes since pressure in aorta is higher than pressure in left ventricle. -in Isovolumic relaxation: all valves are closed. Slide#90: back to slides80,81 and 82 for more details. Slide#91 + Slide#85: “Revision and good test questions” the doctor said. -P wave is atrial depolarization(1). When atrium is filling of blood, the last thing that happens before the mitral valve closes (in the case of left side) , is atrial contraction, it wants to get the blood out as much as possible, so right before the contraction (2) , we have the end diastolic volume (3), QRS means that the ventricle is depolarized (4) and we are going to have that increase in pressure, which is called isovolumic contraction (5) and then you have (when aortic valve is open what happens to the blood in ventricle? ) ejection of blood into the aorta (6) , the volume of ventricle after ejection is called the end systolic volume (7), then the repolarization starts (8) = T wave, then when aortic valve closes, we have isovloumic relaxation (9) , and then the ventricle starts filling (10) and the mitral valve closes. -Remember, Stroke volume is the difference between the end diastolic and end systolic volume and it is very important because it tells you if there is a problem with someone in the heart or a heart failure, because if the heart is not ejecting enough blood to the body, the stroke volume will decrease. But when you are exercising and need more blood and oxygen, the stroke volume increases. -If the end diastolic volume is higher, we have more blood in the heart , and the heart is able to compress and eject more blood. -The heart has a unique mechanism to adjust itself to maintain a normal blood flow. Slide#92: -Physician put the stethoscope on the top part for aortic valve, on the apex for lower valves…. -S3: is usually heard in children. -S4: is related with atrial contraction and if it is heard in adults, it indicates a problem in the heart. (the doctor said that you are not supposed to know S3 and S4) Slide#93: -Oscillation means movement up and down, back and forth. Slide#96: -incisura = dicrotic notch. Slide#101: -When somebody has a heart failure walks or exercises just a little bit, he gets tired, because his heart is not able to pump enough blood for demands of his tissues. Slide#103: -If the EDV=120 ml and the SV=70 ml, the Ejection fraction =70/12 = 5.8. -We use Ejection fraction as another indicator of how well the heart is pumping blood to our body. -Physicians use ejection fraction to see how well the heart is functioning after treating someone with a heart attack. Slide#104: -Remember: if the right ventricle pumps 5L/min, the left ventricle pumps 5L/min. -The average cardiac output= 5 L/ min, this increases when you exercise, or when you take Dr.Iyad’s exam. Slide#106: -It is very important that the heart adapts to the changes that we have, meaning: the blood that is coming from the right side and leaving from the left side of the heart, they have to be equal. -If the blood that comes from the left side to tissues is bigger than the blood comes to the right side, the blood pressure will increase. -Frank-Starling Law: is about having equal amounts of cardiac input and cardiac output. Slide#108: -If our blood is collecting in our veins , we have something called: Edema, which is a collection of fluids. -If we do more exercises, we need more blood, and the tissues of ventricles stretch to have more contraction, so the actin-myosin relationship is optimal, now the atrial wall receives more blood so it stretches and increases the heart rate, which will increase the cardiac output, since it equals to heart rate multiplied by the stroke volume. Slide#109: -Frank-Starling law is involved in pathological situations. Slide#110: -Preload= End diastolic volume. -Contractility will be positively controlled by the sympathetic nervous system. Slide#113: -SA and AV node will be affected mostly by the parasympathetic stimulations. -Hyperpolarization means the membrane potential is more negative, so it will take longer time to get to the threshold. Slide#114: -back to slide#91 for more details. -The pressure during the end of diastole is very low. Slide#116: -We have 70 cardiac cycles in a minute. Slide#117: -when increasing contractility, the stroke volume increases and the end systolic volume decreases. -Decreasing afterload will increase the stroke volume, since we have less pressure in aorta, when the heart starts contracting, the valve will open earlier (instead of 80, it will open at 70), and the blood will start to move the ventricle earlier, so more blood will be pushed out. Slide#119: -Acidosis: increase the H+ concentration and thus increase acidity.