* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download document
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
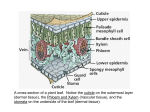
Standard 10 a. By: Brandi and Jamaal All About Plants • Plants are multicellular eukaryotes that have cell walls made of cellulose. • Plants in the Kingdom Plantae • Plants are autotrophs • Plants life cycles have two alternating phases, a diploid (2N) phase and a haploid (N) phase known as alteration of generations • Diploid phase (2N) also known as sporophyte; spore producing plant • Haploid (N) phase also known as the gametophyte, or gamete producing plant Structure of a Plant • • • • • • Roots- help to anchor the plant in the soil so it doesn’t fall over Stems- support the plant; act as the plants pluming system by conducting water and nutrients from the roots and food in the form of glucose from the leaves to other plant parts Leaves- designed to capture sunlight which flowers use to make food through photosynthesis Photosynthesis- the process by which plants, some bacteria, and some protistans, use the energy from sunlight to produce sugar, which cellular respiration converts into ATP the “fuel” used by all living things Flowers- the reproduction part of most plants Seeds- an embryo of a plant that is encased in a protective covering and surrounded by food supply What Do Plants Use To Make Food? Plants uses many different things to make food including: •Chlorophyll which is a green pigment that is in leaves of plants •Light •Carbon Dioxide •Water •Nutrients and Minerals •In photosynthesis, plants release oxygen into the air in which humans and animals breathe. Reproduction • Pollination- the transfer of pollen from a stamen to a pistil; starts the production of seeds • Stamens- the male part of the flower and they produce a sticky powder pollen • Pistil- the female part of the body; • Stigma- the top part of the pistil which is often sticky • Ovule- the base of the pistil where seeds are made Pollination • Plants that are pollinated by animals are often bright colored and have a strong smell to attract the animal pollinators • Plants that are pollinated by wind are pollinated when wind picks up pollen from one plant and carry the pollen to another plant Monocots and Dicots • Two classes within the angiosperms: the Monocotyledonae, or monocots, and the dicotyledonae, or dicots. • Monocots and dicots are named for the number of seed leaves, or cotyledons, in the plant embryo • Monocots have one seed leaf, and dicots have two Cotyledons • Cotyledon- the first leaf or the first pair of leaves produced by the embryo of a seed plant What Plants Need to Survive • Plants use the energy from sunlight to carry out photosynthesis; plants displays adaptations shaped by the need to gather sunlight • All plants require a constant supply of water; plants must obtain and deliver water to all their cells ; plants have certain structures that limit water; as plants absorb water, they absorb minerals • Plants require oxygen to support cellular respiration as well as carbon dioxide to carry out photosynthesis: plants exchange gases with the atmosphere without losing excessive amounts of water through evaporation • Plants take up water and minerals through their roots but make food in their leaves Venation Patterns • Cotyledon venation patterns are described for 93 species • Patterns are grouped into series of levels of complexity according the number of primary vein, nine, seven, six, five, three, or one and three vein patterns are predominate Question 1 1 Which student has correctly classified each plant? STUDENT OAK TREE CORN DANDELION CARROTS 1 2 Monocot Dicot Monocot Monocot Monocot Dicot Dicot Dicot 3 Dicot Monocot Monocot Dicot 4 Dicot Monocot Dicot Dicot A. Student 1 C. Student 3 B. Student 2 D. Student 4 Answer… D.STUDENT 4 Question 2 2 A class observes an unknown plant and discovers that the plant’s seeds have only one cotyledon. When the class examines the leaves and the stem, what will they MOST LIKELY find? A parallel veins and a ring of vascular bundles B parallel veins and scattered vascular bundles C a netted arrangement of veins and a ring of vascular bundles D a netted arrangement of veins and scattered vascular bundles Answer… B. Parallel veins and scattered vascular bundles Question 3 3 A B C D Why are nonvascular plants typically smaller and shorter than vascular plants? Nonvascular plants use mitosis to produce cells. Nonvascular plants use photosynthesis to obtain energy. Nonvascular plants lack tubes to transport materials. Nonvascular plants lack deep fibrous roots to obtain water. Answer… C. Nonvascular plants lack tubes to transport materials Question 4 4 Study the table below. Which statement is correct? Plant Comparison Plant Number of Flowering Arrangement of Vascular Parts 1 Multiples of 3 Number of Tissue in Stem Embryo Parts Scattered 1 2 Multiples of 4 or 5 In a ring A. Plants 1 and 2 are gymnosperms 2 C. Plant 1 is a monocot and plant 2 is a dicot B. Plants 1 and 2 are nonvascular plants D. Plant 1 produces seeds, and plant 2 produces cones Answer… C. Plant 1 is a monocot, and plant 2 is a dicot Question 5 Study the leaf below. A plant with the leafvenation pattern shown would be classified a A.dicot, with two cotyledons B.dicot, with one cotyledon C.monocot, with two cotyledons D.monocot, with one Answer… A. DICOT, WITH TWO COTYLEDONS Question 6 What are the two phases of plants? A. Gametophyte then sporophyte B. Haploid then diploid C. Sporophyte then gametophyte D. Diploid then haploid Answer D. DIPLOID THEN HAPLOID Question 7 What kingdom are plants in? A. The flower kingdom B. Kingdom plantae C. Kingdom fungi D. Kingdom animalia Answer B. Kingdom Plantae Question 8 What is a seed? A. Nutrients that surrounds and protects the embryo B. An organism that is in its early stage of development C. An embryo of a plant that is encased in a protective covering and surrounded by a food supply D. A tiny structure produced by a plant Answer C. An embryo of a plant that is encased in a protective covering and surrounded by a food supply Question 9 What is the first leaf or the first pair of leaves produced by the embryo or seed plant? A. B. C. D. Dicot Gametophyte Monocot Cotyledon Answer D. cotyledon Question 10 Which has a single cotyledon? A. Sporophyte B. Monocots C. Fuit D. dicots Answer B. Monocots Question 11 What are underground organs that absorb water and minerals? A.Veins B.Leaves C.Nutrients D.roots Answer D. ROOTS Question 12 What are plants considered? A. Autotrophs B. Monotrophs C. Hetertrophs D. green Answer A. autotrophs Question 13 Are plants eukaryotes or prokaryotes? Answer Eukaryotes Question 14 What are the two types of reproductive cells? A. Embryos and stems B. Nutrients and minerals C. Sunlight and carbon dioxide D. Gametes and spores Answer D. Gametes and spores Question 15 What are veins made of? A. Leaves and roots B. Stems and tracheids C.Xylen and phloem D.Lignin and vascular tissue Answer C. Xylen and phloem