* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Formulas
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
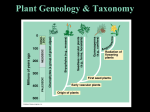
Plants Adaptations Non-Vascular Gymnosperms Angiosperms Vessels Phloem Most modern plants contain vessels to transport water up, and sugars down. Phloem “flows” and xylem go the other way. Vessels allow trees such as the Giant Sequoia to be over 100 ft tall and still get water from the soil. Vessels Rings and grains we see in crosssections of wood are their vessels. More xylem and phloem form as the tree grows and requires more transport. Another ring of vessels is formed every year. Mountain Mahogany Wood Non-vascular Non- without Vascule- vessel Plants that predate xylem and phloem have limited environmental options – Moist habitats – Near streams or rivers – Temperate or tropical rainforests – Close to low running water (short plants) Non-vascular http://www.square-mag.co.uk/2009/02/02/nguyen-la-chanhcreates-the-moss-carpet/ Non-vascular First plants on land were non-vascular Fossils identified as non-vascular plants appear in rocks from 440mya No actual roots or stems, no vessels Gametes are dispersed by water (no seeds) – Sperm literally swim in water droplets over to the female egg and fertilize to produce a new plant In moderate to dry soils, non-vascular plants cannot absorb enough water to survive Vascular First vascular plants were club mosses that grew to tree-size. Has roots, stems, and leaf-like structures Still around today, but not so big Vascular Vascular plants began to show great diversity. Many primitive vascular plants are still around today. With roots, stems, and leaves, they could live in many places non-vascular plants could not. Vascular According to fossil evidence, ferns showed up about 375 mya when club moss and horsetail were the dominant vascular plants. These ferns were treesized, but soon began to diverge Today they are more abundant than their primitive competitors. Seeds Seed plants produce spores like non-seed plants Males produce pollen grains that contain two sperm each Female produce eggs contained within ovules When the sperm reaches the egg, fertilization takes place and a plant is “born.” Gymnosperm “naked seed” Seeds not protected by a fruit Seeds often are on the scales of woody cones (conifers) Male cones release pollen Female cones have eggs Gymnosperms Ginkgo males produce pollen Ginkgo females make a fleshy seed coat that stinks when crushed Very smog tolerant Last surviving ginkgo- Gingko balboa Gymnosperms Conifers- cone producing plants Typical gymnosperm Sometimes known as evergreens because some are not deciduous Often needle-like leaves “pine” scent Angiosperms “flowering plants” Produce flowers AND form seeds enclosed in a fruit Fruit helps aid in seed dispersal as animals feed on it. Fruit is formed from the flower’s female reproductive structures.