* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Angiosperms
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
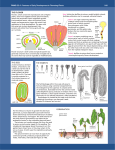
First flowering plants Angiosperm: flowering plants vascular heterospory male vs. female gametophytes flower specialized structure for sexual reproduction seeds within fruit pollen life cycle dominated by sporophyte stage trees & bushes are diploid reduced (microscopic) gametophyte Angiosperms Anthophyta More specialized xylem evolved. Tracheids seen in gymnosperms gave rise to vessel elements Seeds are no longer “naked” Xylem is reinforced by second cell wall, the fiber (also seen in conifers) Flower is the reproductive structure Coevolution is seen between flowers and animals Identify the flower structures… Flower variations The Fruit What is a fruit? After fertilization the ovary becomes the fruit. It protects the seeds. Name three modifications that different fruits have for seed dispersal. 1. 2. 3. Sweeten and turns colorful when ripe Have burrs that can sticks to animal’s fur Feathery like dandelions for wind dispersal of seeds Angiosperm: fruiting plants Other fruits… Seed Dispersal Sporophyte/Gametophytes The life cycle of the anigosperms shows very reduced gametophyte generations. What is the male gametophyte? What is the female gametopyte? What is pollination? Bringing pollen to the stigma. How does self-incompatibility work? Angiosperm Life Cycle Double Fertilization The pollen tube grows following pollination and leads to double fertilization. What is fertilized? Sperm + egg = zygote (2n) Sperm + 2 polar nuclei = endosperm (3n) Seed Development Endosperm develops before embryo Endosperm provides food for developing embryo Embryo reaches a certain size and then enters dormancy until germination. Seed & Plant embryo Seed offers… protection for embryo stored nutrients for growth of embryo endosperm (3n) cotyledons embryo (2n) cotyledons = “seed” leaves, first leaves of new seed coat Germination • • • How can seed dormancy be advantageous to a plant? Helps with dispersal Doesn’t leave dormancy until conditions are good What are some conditions for breaking dormancy? Desert – Only after good rainfall Chaparral – fire Others – coats weakened by digestive enzymes as they pass through animal’s digestive tract Imbibation Hormone release … Radicle emerges from seed Shoot tip breaks through the soil. Until this point how has the embryo received nutrients? Endosperm(food)and radicle (water). Review the Evolution of Alternation of Generation in Plants Monocots & dicots Angiosperm are divide into 2 classes dicots (eudicot) 2 cotyledons (seed leaves) leaves with network of veins woody plants, trees, shrubs, beans monocots 1 cotyledon leaves with parallel veins grasses, palms, lilies Flower Bud xs 8 nucleate embryo sac Pollen grain has 2 cells: • Generative cell • Tube cell Co-evolution: flowers & pollinators How a bee sees a flower…insects see UV light = a bulls-eye to the nectar