* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Growing Seeds - Etna FFA Agriculture
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
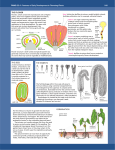
G S rowing eeds One of life’s little wonders… Things to ponder… What are the 5 major plant growth requirements? Nutrients Light Moisture Carbon Dioxide Temperature It’s just a seed right? Dry Small Ugly Who cares? Or is it? All Different Alive Little promises of growth! Hold Potential Impressive Neatly packaged What is a seed? A seed is a fertilized, ripened ovule of a seedproducing plant… Containing a living plant embryo capable of germinating and producing a new plant! More simply… A seed is a guarantee of another plant! How are seeds formed? Flowers are pollinated and seeds form within the drying flower. What’s in a seed? A tiny living plant embryo suspended inside. What’s viability? This ability for the embryo to wait suspended is called “viability” Epicotyl: (in the embryo of a plant) the part of the stem above the cotyledons. Hypocotyl: connects the cotyledons to the radicle. Radicle: The part of a plant embryo that develops into a root. Cotyledon: the primary leaf of the embryo of seed plants. (Like the sepal of a bud… for protection.) What is the length of a seed’s viability called? “longevity” The 2 Seed Categories: Monocot One seed leaf Flower parts are in 3’s or multiples of 3 Leaves have parallel veins Vascular bundles are scattered in the stem Tap Root System Monocot Seed Coat Endosperm Cotyledon Embryo Dicot Two seed leaves (cotyledons) Flower parts in four or five multiples Leaves are net veined Vascular bundles in stems are arranged in a circle Fibrous Roots Seed Coat Endosperm Cotyledons Embryo Dicot Can you tell them apart? A B Can you identify the parts? #3 #1 #4 #2