* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Anatomy & Physiology
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
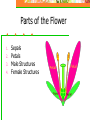
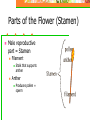
Plants Structure and Function Sexual Reproduction Flowers Function Contain the sexual organs for the plant. Produces fruit, which protects, nourishes and carries seeds. Attracts insects for pollination. Parts of the Flower 1. 2. 3. 4. Sepals Petals Male Structures Female Structures Parts of the Flower Sepals Outer covering of the flower bud. Protects the stamens and pistils when flower is in bud stage. Modified leaves. Often green. Parts of the Flower Petals Modified leaves Brightly colored Protects stamen & pistils. Attracts pollinating insects. Carries pollen from one flower to another. Parts of the Flower Petals of plants that have wind pollination: Small sepals/petal or none at all. Parts of the Flower (Stamen) Male reproductive part = Stamen Filament Stalk that supports anther Anther Produces pollen = sperm Parts of the Flower (Pistil) Female reproductive part = Pistil (3 parts) Stigma Sticky top Holds the pollen grains Style tube Ovary Enlarged portion at base of pistil. Produces ovules (eggs). If fertilized, develops into seeds. Parts of the Flower Pollination • Wind or animals • Pollen reaches stigma • Fertilized Egg = Seed • Seed Coat: Protection • Seed Leaves • Developed from embryo • Monocot: 1 leaf • Dicot: 2 leaves • Endosperm: food supply for embryo Pollination • Fruit-Ovary Tissue • Seed develops here • Examples: • Apple, watermelons, cherries, vegetables, grains, nuts, tomatoes, cucumbers • Help with seed dispersal so doesn’t compete with parent Dispersal Animals: • Tasty • Eat and then poop out with fecal fertilizer. • Sticky • Ride away on • Ex. Burrs Wind/Water • Parachute/Wings • Cottonwood • Float • Coconuts Dormancy Until the right environment is available: • Temperature • Moisture • Oxygen • Light Survive animal digestive tracts while softening the seed coat. Germination Steps: 1. Seed coat cracks and embryonic root breaks through. 2. A young shoot breaks through surface of soil. 3. Leaves grow from shoot and begin to photosynthesize Seedling