* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Evolution - Cloudfront.net
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
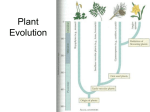
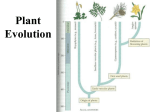
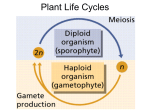
Plant Evolution Plant Evolution • Evolved from green algae (450 mya) • Green algae ancestor – Multicellular body – Cells w/ channels to communicate – Reproduce w/ sperm & egg • Early plants – Low growth (nonvascular) Land Adaptations • Retain Moisture – Early plants grew near waters edge – Cuticle: waxy coating Land Adaptations glucose water • Transporting Resources – Vascular system: tissue to transport nutrients • Up from the roots (ex: water) • Down from the leaves (ex: sugars) – Allows taller growth Land Adaptations • Growing upright – Large plants need to support own weight – Lignin: hardens cell wall; gives wood strength Land Adaptations • Reproduction on land – Pollen: carried by wind/animals – Seeds: hard coat protects embryo inside Alternation of Generations X X X X X • Diploid Stage – zygote created from sperm & egg – Zygote grows into a sporophyte – Meiosis makes spores • Haploid Stage – Male gametophyte creates sperm – Female gametophyte creates egg • Diploid stage restarts: Sperm and egg make a diploid zygote • The cycle repeats Kobe Kuiz 1) What traits do plants and plant-like protista share? 2) Name 4 adaptations that plants have for life on land. 3) Which plant adaptation allows them to carry nutrients to great heights? 4) Which plant adaptation allows them to retain moisture? 5) What is the purpose of lignin? 6) What is the chromosome combination for the sporophyte stage? 7) What is the chromosome combination for the gametophyte stage? 8) What does the gametophyte stage create? 9) What does the sporophyte stage create?