* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plants - Chatt
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
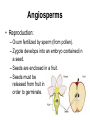
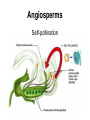
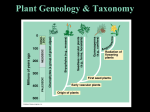
Plants Characteristics • • • • Eukaryotic. Multicellular. Photosynthetic. Cell walls contain cellulose. • Develop from embryos protected by parental tissue. Earliest Ancestor • The earliest land plants may have evolved from algal-like organisms. Generalized Life Cycle • Alternation of generations. – Gametophyte generation (n). – Sporophyte generation (2n). Plant Types • Non-Vascular (bryophytes) • Vascular (tracheophytes) – Spore-producing – Seed-producing Non-Vascular Plants • • • • • Includes mosses, liverworts and hornworts. Lack true roots, stems, leaves and vascular tissue. Grow in moist environments. Only several centimeters in height. Sexual (spores) or asexual (vegetative propagation). Vascular Plants • Conducting tissue. – Xylem & phloem. • Allowed greater heights in plants. Spore-Producing Vascular Plants • Includes club mosses and horsetails. – Primarily grow in marshes and along edges of streams. • Includes ferns. – Primarily grow in shady, wet environments. Reproduction in Non-Vascular & Spore-Producing Vascular Plants Both require water for the sperm to swim from antheridium to archegonium to fertilize egg. Fern sperm Seed-Producing Vascular Plants • Most successful plants on Earth. – Due to specialized leaves, stems and roots. • Sexual reproduction occurs via pollination. – Does not require water. – Seeds withstand desiccation. • Includes: – Gymnosperms. – Angiosperms. Gymnosperms • Reproductive structures. – Pollen cones (male). – Seed cones (female). • Pollen dispersed by wind. • Pollen produces sperm when contact is made with seed cone. • Sperm fertilizes ovules. • Zygotes grow into seeds. Watch This!!! Gymnosperms Conifers are the most numerous. Conifers • Referred to as “softwood”. • Accounts for 50% of Ontario’s forests. • Canada supplies 20% of world’s softwood. Angiosperms • Known as the flowering plants. • Most successful plants on Earth. – Well-protected seeds. – Variety of seed dispersal mechanisms. • Wind, water or animals. Angiosperms • Reproduction: – Ovum fertilized by sperm (from pollen). – Zygote develops into an embryo contained in a seed. – Seeds are enclosed in a fruit. – Seeds must be released from fruit in order to germinate. Angiosperms Self-pollination Angiosperms Cross-pollination Watch This!!! And This!!!