* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pest Insect and Pest Insects are small animals that have three body
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
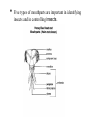
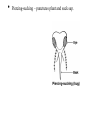
Pest Insect and Pest Insects are small animals that have three body regions and three pairs or six legs. Body regions are head, thorax and abdomen. • Five types of mouthparts are important in identifying insects and in controlling insects. • Chewing—tear, chew or grind food. Examples: grasshoppers, beetles. • Piercing-sucking – punctures plant and suck sap. Aphid Mosquito • Rasping-sucking—rasps or break surface and suck sap. Example: thrips. Tomato spot wilt disease Siphoning—have a coiled tube they dip into liquid food such as nectar and draw it in. • Sponging—have two sponge-like structures that collect liquid food and move it into the food canal. Example: Housefly. Life Cycles for insects • Complete metamorphosis has four stages: a. Egg. b. Larva—worms or caterpillars. c. Pupa. d. Adult—flies, beetles, etc. • Incomplete metamorphosis has three stages: a. Egg. b. Nymph. c. Adult. • Chewing pest a. Beetles—eat leaves, stems, flowers, fruit and nuts. b. Cutworms—usually attack stems, but may eat other plant parts. c. Caterpillars—larva of moths and butterflies and are fuzzy or hairy. Eat young leaves and stems. Roll up in leaves making leaves curl. d. Grasshoppers—eat all parts of plants. Cucumber beetle Cutworms Caterpillars Grasshoppers Shucking pest • Aphids • Leaf bug • Mealy bug • Scale • Thrips • Whitefly • Mites Diseases Blights cause plants to quickly turn brown or black as if they had been burned. Canker causes open wounds on woody plant stems. Damping off is a fungal diseases that causes young plants and seedlings to rot off at soil level. ONLY IN SEEDLINGS Galls are round swellings or growths on plants. Mildew grows on leaf surfaces—both upper and lower-as white, gray or purple spots. Mosaic is caused by viruses that make the leaves have irregular mottled areas with patterns ranging from dark green to light green to yellow to white. Rots cause plant to decay and die. Rust cause small spots on leaves that resemble yellow, orange, brown or red rust mainly on the underneath side of leaves . Smut is a black powdery disease that causes blisters that burst open releasing black spores. Wilts are diseases that block the uptake of water in plant stems causing plants to wilt. Disease is a plant disorder caused by an infectious pathogen or agent . Three conditions necessary for diseases in plants. 1. Host plant. 2. Disease causing organism or pathogen must be present. 3. Favorable environment for disease organism to develop. Groups of Pathogens. 1. Bacteria. 2. Fungi. 3. Viruses. 4. Parasitic plants-mistletoe, dodder, lichens attach to plant. Plant diseases must be identified before they can be treated. Warm temperatures and moist conditions in greenhouse plant production make most horticulture plant diseases worse because of environmental conditions that support disease-causing pathogens. Preventing plant diseases is better than treating the diseases. Biological uses natural enemies such as birds, other insects, etc. Contact poisons affect the insect’s nervous system and must come into contact with insect to be effective. Acephate Deltamethrin Carbaryl Fumigants are poisonous gases released into an enclosed place so that insects breathe the gases. Stomach poisons are sprayed on plant surfaces or are taken into the plant through absorption. The insect must eat or suck the poison to get it into the stomach for this method to be effective. Systemic poisons are more effective for controlling sucking insects. Cultural involves sanitation, removing insect breeding and hiding areas and using insect resistant plant varieties. Mechanical uses physical control such as insect traps using screens over fans and other openings and washing plants with soapy water. Natural methods use natural barriers such as rivers, woods, mountains and predators to control insects. Quarantine physically isolates insects from healthy plants. IPM Intergraded pest management Name and address of manufacturer. Trade name. Active ingredients including official common name or chemical name of each ingredient. Type of Pesticides—herbicide, insecticide, fungicide, etc. Form of substance—dust, wettable powder, fumigant, etc. • Storage and disposal precautions. H. Hazard statement including ‘Keep Out of Reach of Children”. I. Directions for use—mixing, application, etc. J. Net contents. K. Statement of practical treatment states what to do if a person swallows or is poisoned by spilling the chemical on the skin. L. Worker protection procedures including reentry time on how long before a person can enter the treated area. Signal words—toxicity levels for humans. 1. Danger—has skull and crossbones symbol and poison on label. Highly toxic, most poison or lethal dosage. 2. Warning—moderately toxic. 3. Caution—slightly toxic to non-toxic. The most important safety rule is “read and follow label directions” because all the rules are included in this one rule.