* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Characteristics of Seed Plants
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
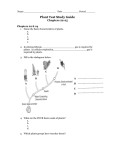
The Characteristics of Seed Plants Chapter 10 Section 3 Why do scientists believe in these supposed relationships? We do see varietal variation, but no transition from one major kind of plant into another. Seed Plants Seed plants share two important characteristics. They have vascular tissue, & they use pollen & seeds to reproduce. They all have body plans that include leaves, stems, and roots. Water, food and minerals are transported throughout plants in vascular tissue. Two types of Vascular Tissues Xylem & Phloem Phloem is the vascular tissue through which food moves. When food is made in the plant’s leaves, it enters the phloem & travels to other parts of the plant. Water & minerals travel in the vascular tissue called xylem. The plant’s roots absorb water & minerals from the soil. These materials enter the root’s xylem & move upward into the stems & leaves. Seed plants can live in a variety of environments. They produce pollen, tiny structures that contain the cells that later become sperm cells. Pollen delivers sperm cells directly near the eggs, therefore seed plants do not need water for fertilization to occur. Pollen Bee covered in pollen. Seeds are structures that contain a young plant inside a protective covering. Inside a seed is a partially developed plant. If a seed lands in an area where conditions are favorable, it sprouts out of the seed & begins to grow. A seed has three main parts- an embryo, stored food, & a seed Seeds Seed Plants The young plant that develops from the zygote, or fertilized egg, is called the embryo & has the beginnings of roots, stems, & leaves. The embryo also has one or two seed leaves, or cotyledons. In some seeds, the cotyledons store food. The outer covering of a seed is called a seed coat. A seed may remain inactive for awhile. Germination Germination occurs when the embryo begins to grow again & pushes out of the seed. Environmental conditions, such as temperature & moisture, must be just right in order for a seed to germinate.