* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tropism - Cloudfront.net
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
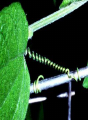
Chapter 25 25-2 Plant Responses I. Tropisms A. Tropism is a slow plant movement, towards or away from a stimuli, that is determined by the direction of an environmental stimulus. 1. 2 Types a. Positive tropism – movement towards a stimuli. b. Negative tropism – movement away from a stimulus. 2. Phototropism A. A plant movement in response to light. 1. Light causes hormone Auxin to move to the shaded side of the shoot, elongating those cells causing the plant to lean towards the light. a. Solar tracking – leaves tracking the sun’s light and moving with the sun across the sky. 3. Thigmotropism A. A plant’s growth response to touch or touching a solid object. Some plants coil when they touch an object like the growth of vines. 4. Gravitropism A. A plants growth response to gravity. 1. Positive gravitropism – roots grow down with the gravitational pull. 2. Negative gravitropism – stem growth up and away from the gravitational pull. 5. Nastic Movement A. A. A plants rapid movement that occur in response to environmental stimuli that are independent of the direction of the stimuli. These movements are regulated by changes in the water pressure of certain plants. 6. Thigmonastic a. Venus Fly Trapa combination of osmotic pressure and cell wall expansion causes the leaf to snap shut. 7. Nictinastic A. Nictinastic – plants movement in response to the daily cycle of light and dark. Turgur pressure is more gradual. 8. Photoperiodism a. Timing of seasonal activity such as flowering and growth. Phytochrome, a plant hormone is said to be responsible for photoperiodism. 1. Short-day plants – flower when the days are short. 2. Long-day plants – flower when the days are long.