* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cool Things that Plants Do
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
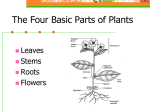
Cool Things that Plants Do AP Biology - LAHS Cool Things that Plants Do 1. Organ Modification 2. Movement 3. Clonal Colony 4. Grafting 5. Really really cool plants 1. Organ Modification Plants have organs: stems, roots, leaves, etc. All stems must have buds/leaves to be classified as stem tissue Stolon: horizontal stem that is fleshy or semi-woody and lies along the top of the ground (strawberries) Bulbs: shortened stems surrounded by fleshy scales (modified leaves) that envelop a central bud located at the tip of the stem (garlic, onion) 1. Organ Modification Tubers: swollen portions of underground stems (stolons) stems have nodes, and buds arise at nodes Potatoes Pneumatophores: spongy outgrowths of underwater roots (plants in swamps) Facilitate oxygen supply 1. Organ Modification Buttress Roots: provide stability Parasitic Roots: stems that lack chlorophyll will produce roots that penetrate host plants 1. Organ Modification Floral Leaves (bracts): surround the true flowers and perform the same function as showy petals Poinsettias and dogwoods Spines: reduction of leaf surface reduces water loss and deters predators Not to be confused with thorns cacti 1. Organ Modification Floating Leaves: Water lilies Evolved to have very large area to float on water Victoria amazonica Leaves can grow to over 2.5 m across Network of protruding ribs on underside of leaf for buoyancy and stability The leaves are rumored to be able to hold a baby 1. Organ Modification Insectivorous Leaves: leaves trap insects and digest their soft parts plants that need nitrogen Nutrients are absorbed through the leaf surface Pitcher plants Sundews Venus Fly Trap Almost 200 species of flowering plants that are insectivorous 2. Movement Plants move via tropisms – slow movement Plants move for other reasons and can be perceived with the naked eye – rapid plant movement Venus fly trap Mimosa “Telegraph Plant” 2. Movement Youtube Videos: Moving Mimosa Plant http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wAN9ejXyhV8 Venus Fly Trap http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kRUaJD0oT6A&NR=1&fe ature=fvwp Telegraph Plant “Dancing Plant” http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sgQ5CucGz2M 3. Clonal Colony Genet: group of genetically identical individuals that grew vegetatively from a common ancestor An individual of this population – ramet Each colony shares single root structure Quaking Aspen (Populus tremuloides): usually propagates through cloning 3. Clonal Colony Quaking Aspen Sexual reproduction not common, since all individuals are all only 1 sex Pando “The Trembling Giant” Utah Heaviest known organism (est. 6,000 tons collectively) 107 acres 47,000 stems Is claimed to be 80,000 yrs old 4. Really really cool plants Rafflesia arnoldii (Corpse Flower) Produces largest individual flower on earth Flower smells like rotting flesh Lives as a parasite Has no visible roots/stems Does not have chlorophyll Only visible in flowering state Attracts flies for pollination 4. Really really cool plants Polypodium polypodioides “Resurrection Fern” Can survive long periods of drought by curling up and appearing desiccated Will revive within 24 hours after soaking in water Can survive an estimated 100 years of drought and still “resurrect” after a single soaking 4. Really really cool plants Romanesco Broccoli Brassica oleracea Edible flower species Varient of Cauliflower Each bud has smaller buds that occur in a spiral All buds together occur in an even larger spiral