* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Asexual Reproduction in Plants
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
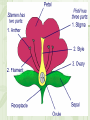
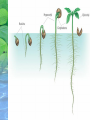
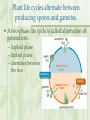
Sexual Reproduction in Plants • Involves production of haploid gametes What is the function of this fruit? Asexual Reproduction in Plants •Produces offspring genetically identical to parent •Also known as vegetative reproduction Methods A. Stolons, or runners: horizontal, above-ground stems example: Bermuda grass, strawberries B. Bulbs: underground stems with modified leaves examples: onion, daffodil, tulip C. Rhizomes: horizontal, underground stems examples: ferns, irises D. Tubers: underground stems example: potato Germination • Water and oxygen are needed for a seed to sprout. • Germination: process in which a plant embryo resumes its growth. • The first sign of germination is the emergence of the root, or radicle Plant Growth and Development I. Nutrients 1. Carbon dioxide and water for photosynthesis 2. Oxygen for cellular respiration 3. Minerals needed for growth Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium Magnesium for photosynthesis II. Hormones 1. Auxin is a growth-promoting chemical that causes stems to bend. Auxin accumulates on the dark side of a plant and causes the cells to elongate. http://www.kscience.co.uk/animations/auxin.htm 2. Another hormone is ethylene, which is a gas. Ethylene stimulates fruit ripening. 3. Cytokinins – stimulate cytokinesis, or cell division. 4. Gibberellins – produce dramatic increases in size Environmental Influences I. Tropisms: responses in which plants grow either toward or away from a stimulus A. The bending of a plant toward the light is a positive phototropism. B. The downward growth of roots is a positive gravitropism. C. The upward growth of shoots is a negative gravitropism. D. Thigmotropism is a response to touch. Coiling of a vine around a trellis is a positive thigmotropism. II. Nastic movements are rapid, reversible responses to non-directional stimuli. Examples include opening and closing of flowers and closing of a Venus fly trap III. Photoperiodism • The response of a plant to the length of days and nights. • Long-day plants produce flowers when days are longer than a certain number of hours. • Examples: Irises • Short-day plants produce flowers when days are shorter than a certain number of hours. • Examples: Poinsettias • Day-neutral plants do not require specific day lengths to flower. Examples include roses, potatoes Plant life cycles alternate between producing spores and gametes. • A two-phase life cycle is called alternation of generations. – haploid phase – diploid phase – alternates between the two SPOROPHYTE PHASE fertilization meiosis GAMETOPHYTE PHASE – moss gametophytes look like green carpet – moss sporophytes shoot up as stalklike structures sporophyte (2n) capsule spores (1n) gametophyte (1n)