* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download plant parts - Horace Mann Webmail
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Philodendron wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
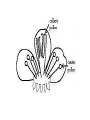
PLANT PARTS The four main plant parts are roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. Each part has a unique structure and function. The plant’s vascular system is found in roots, stems and leaves. These tube-like structures carry water and dissolved nutrients through the plant. XYLEM - carries water and minerals from the roots up PHLOEM - carries nutrients down through the plant from the leaves Why do water and nutrients move in these particular directions? The vascular bundles in a stem contain the xylem and phloem. Where would xylem and phloem be found in a leaf? Let’s start with roots. What jobs do roots do? They: 1.) support and anchor the plant 2.) absorb water 3.) store food ( in the form of starch) Can you name some roots that we eat? Parts of a root Root cap - provides protection for growing root Epidermis - protective layer covering entire root Root hairs - help to absorb water and minerals Cambium cells - in center of root; divide to produce more xylem and phloem Roots can be taproots (one main root) or fibrous (many small roots.) STEMS What jobs do stems do? They: 1.) support the plant. 2.) hold leaves up to the light. 3.) contain xylem and phloem. 4.) may store water and starch. Herbaceous stems are green, soft and flexible, like a flower stem. Woody stems are brown and rigid, like a tree trunk. LEAVES What jobs do leaves do? They: 1.) capture light. 2.) carry out photosynthesis 3.) carry out gas exchange. The size and shape of leaves may change with their needs and environment. This is a cross-section of a leaf. Cuticle - waxy, protective layer Epidermis - protective skin Mesophyll - spongy layer where photosynthesis occurs Veins - contain xylem and phloem Stomates - openings on leaf bottom; gas exchange These are stomata as seen under a microscope. The opening is protected and controlled by guard cells. When the guard cells are full of water, they open the stomate. When they have less water, they are smaller and the stomate is closed. Transpiration - loss of water vapor through stomata Stomata are usually open during the day and closed at night. Can you explain why? FLOWERS What jobs do flowers do? They carry out reproduction. Petals - colorful to attract pollinators Sepals - protective covering of flower bud Stamen - male reproductive part; produces pollen; consists of: a.) filament (stalk) b.) anther (top) Pistil - female reproductive part; contains ovules; becomes seed bearing fruit; consists of: a.) stigma (sticky top) b.) style (tube pollen travels down) c.) ovary ( where fertilization occurs) Pollination - pollen is transferred from anther to stigma How might pollination occur? Fertilization - pollen travels down style (pollen tube) to ovary Where pollen and egg meet; becomes a seed and ovary becomes fruit Perfect flowers have both pistils and stamens. Imperfect flowers have pistils OR stamens.