* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Life Cycle of a Plant
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
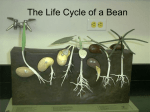
Life Cycle of a Plant How living things grow, live, and die 2nd grade Science Core Content SC-04-3.4.3 Students will compare a variety of life cycles of plants and animals in order to classify and make inferences about an organism. Plants and animals have life cycles that include the beginning of life, growth and development, reproduction and death. The details of a life cycle are different for different organisms. Models of organisms’ life cycles should be used to classify and make inferences about an organism. Vocabulary Life Cycle – a series of stages that a plant passes through from seed, seedling, mature plant, and death. Reproduce – the process by which a plant makes more seeds. Seed coat – covers the outside of the seed to protect the tiny plant. Germinate – when a seed begins to grow because it has soaked up enough water and sunlight. Flower – the reproductive structure of the plant. Pollination – happens when pollen is moved from a stamen to a pistil. The flower then begins to make fruit and seeds. Dormant – the stage where the seed is alive, but not growing. Usually in winter. Stage 1 •Most plants begin their life cycle with a seed. •A tiny plant and seed food is inside every seed. •A seed coat covers the outside of the seed and protects the tiny plant inside. Stage 2 When the seed gets enough warmth and moisture, it germinates or sprouts. The seed soaks up water, and the seed coats splits open. The seed sprouts. A root grows down into the soil and a little shoot grows up toward the sunlight Stage 3 As the roots grow, a stem will also appear. The bean uses the food in the seed to grow. Leaves will grow on the stem and the plant will stretch toward the light. At this stage, the plant is called a seedling and it can use photosynthesis to make its own food. Stage 4 The plant will begin to develop flowers. The flower’s function is to reproduce to make new seeds. Stage 5 After pollination, the flower will turn into a pod with the seeds inside. Many plants also develop fruit, which covers and protects the seed. When the seed has fully developed, the cycle begins again. Bean Seed Life Cycle The Life Cycle of a Plant Use the life cycle diagram sheet. Draw what happens during each of the five stages of a plant’s life cycle. Be sure to explain what happens during each stage.