* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PLANTS - Bishop Ireton High School
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
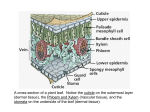
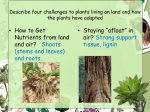
PLANTS Characteristics • • • • Eukaryotic, multicellular, nonmotile Photosynthetic- autotroph Have chloroplast:chlorophyll a and b Cell wall made of cellulose- protects and supports • Cuticle- waxy covering that prevents desiccation Life Cycle • 2 alternating cycles • 2N- diploid sporophyte • 1N Haploid gametophyte Plant Needs • • • • Sunlight Water and minerals Gas Exchange Movement of water and nutrients Plant Adaptations How did plants move from water to land? 1. Vascular tissue: xylem carries water from roots, phloem carries food made in leaves 2. Cuticle—prevents water loss 3. Roots- anchor the plant, absorbs water and nutrients 4. Pollen- male sperm- doesn’t need water to distribute 5. Seeds- provide protection and food supply to embryo 4 MAIN TYPES OF PLANTS Bryophyte Pterophyte Gymnosperm Angiosperm Common Name MOSSES FERNS PINES FLOWERING Vascular tissue No Yes Yes Yes Male gamete Flagellated sperm Flagellated sperm Pollen Pollen Dominant Gametophyte Sporophyte Sporophyte Generation Sporophyte Mosses • No vascular tissue and produce flagellated sperm- so need to be in close contact with water • No roots- rhizoids anchor to ground • Peat moss- used for fuel Ferns • Flagellated sperm • Has vascular tissue Gymnosperm • Vascular tissue • Has male and female cones • Male cone produces pollen • Female cone produces ovules Angiosperm • Produce flowers • Produce seeds within a “fruit” • Vascular tissue • Green(Herbaceous) or woody stem 2 Types of Angiosperms • Monocot- Grasses, lilies • Dicot-Shrubs, trees, flowers • Annuals- live 1 year, have herbaceous or green stem(replant) • Perennial- trees and shrubs • Biennial- takes 2 years to grow-root storage like carrots Monocot vs. Dicot Vascular Bundle Vascular Bundle Vascular Bundle in Leaf in Stem Cross in Root Cross section Section Flower groups Monocot Parallel Scattered Ring 3’s Dicot Web like Ring X 4’s and 5’s 3 Types of Plant Cells • Parenchyma- storage and food production • Collenchyma- found in areas of current growth • Sclerenchyma- thick walled cells used for support, also fiber, and grit in pears 3 Types of Plant Tissues 1. Dermal- makes up epidermis-protects- secretes cuticle 2. Vascular- set of “pipes” that transport materials far distances. Xylem carries water (tracheids and vessel elements) Phloem carries food(sugar)(sieve tube elements and companion cells) 3. Ground – sites of photosynthesis(leaves), storage(roots), and support(stems) Plant growth Meristematic tissue- site of actively dividing cells(mitosis). Found at tip of shoot(called apical- at the top) and the tip of the root. Apical meristem found at the top of the shoot and bottom of the root. Plant organs • Roots • Stems • Leaves Roots • help anchor plant, absorb nutrients, have root hairs to increase surface area • 2 types- fibrous taproot (food storage like carrot) Monocot (vascular bundle arrangement ) Dicot • Root cap at end of the root- protects new ,growing cells. Also produces lubricant so root can move through soil. Stems • Support the leaves • 2 types- herbacous- green • woody • Monocot (vascular bundle arrangement) Dicot Leaf • Site of photosynthesis • Palisade mesophyll and spongy mesophyllphotosynthesis cells. • Spongy mesophyll loosely packed – spaces where the gases can be stored. • Vascular bundle contains the xylem and phloem • Stomata open during times when water loss is low(early day or late afternoon) • Loss of water through stomata called TRANSPIRATION Stomata- opening in the leaf that allows gas exchange- O2 out and CO2 in for photosynthesis. Guard cells control the opening of the stomata. When guard cells fill with water, stomata open. When water leaves guard cellsstomata are closed. Water transport • What moves water up against gravity? • Root pressure- movement of water coming up from the roots • Adhesion- water sticks to sides of xylem cells • Capillary action- water attracted to itself and the tube • Transpiration- when stomata open- help pull the water up- negative pressure STOMATA Flowers • Reproductive organ of a plant- contains the male and female parts • Plants do not self fertilize- mechanisms in place that doesn’t allow it. • Male- stamen (anther and filament) • Female –carpel (stigma, style and ovary) • Petals- attract pollinator • Sepal- green leaf surrounding flower Plant Hormones • Auxin- cell elongation • Gibberellins- promote growth • Cytokinin- stimulate cell division,growth of lateral buds • Ethylene gas- promotes fruit ripening Tropism• plant response to external stimulus like light or gravity • Thigmotropismresponse to touch-vines Photoperiodism Short Day Plants • Short day, long night • Can interrupt night to stop flowering • Poinsettia Long Day Plants • Long day, short night • Increase night to stop flowering • Iris