* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PLANTS
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
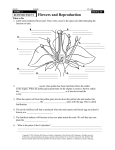
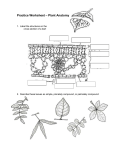
PLANTS LIFESPAN • ANNUAL: live < 1 yr • BIENNIAL: live 2 yrs • PERENNIAL: live > 2 yrs GROWTH FORMS • GRASS • FORB/HERB: not woody • SHRUB: woody, small • SUCCULENT: stores water in tissue • TREE: woody, tall FLOWERS • • • Sex organ of plant From modified leaves Consists of four rings of structures – 1. Sepals: protect flower bud – 2. Petals: attract pollinators FLOWERS 3. Stamens: male – produce sperm – consist of… Anther: produces sperm and packages into pollen grains Filament: Holds anther into air to contact pollinator FLOWERS 4. Pistil: female – produce eggs • Stigma: accepts pollen • Style: hold stigma up to contact pollinator • Ovary: produces eggs/seeds TYPES OF FLOWERS Perfect: have functioning stamens and pistil Imperfect: have either functioning stamens or pistil TYPES OF PLANTS With Imperfect Flowers Dioecious: Monoecious: two houses (male and female flowers on separate plants) one house (male and female flowers on same plant) Male Plant e.g., bursage Female Plant e.g., desert broom, jojoba, sotol LEAVES LEAF PARTS Blade Petiole Expanded Leaf Base BLADE STRUCTURE Simple: Compound: blade is single blade divided into leaflets • Palmately Compound: leaflets come out of one point BLADE STRUCTURE • Pinnately Compound: • Bipinnately Compound: just primary leaflets blade divided into primary expanded leaf base petiole and secondary leaflets e.g., Velvet Mesquite e.g. Desert Ironwood BLADE STRUCTURE: Quiz yourself Pinnately compound Bipinnately compound Tripinnately compound Bipinnately compound Palmately compound Simple Palmately compound Pinnately compound BLADE EDGE Entire: Lobed smooth Toothed POSITION OF LEAVES ON STEM Alternate Opposite Whorled 1 leaf comes off each point on stem 2 leaves come off same point on stem 3+ leaves come off same point on stem FLOWERING PLANT LIFECYCLE www.cactus-art.biz • GERMINATION: Sprouting of seed – Timing is Critical! – Cues include photoperiod, temperature, moisture, light, abrasion, fire, digestive enzymes, etc. • GROWTH: from seedling to maturity • REPRODUCTION: production of next generation • DEATH: annual vs biennial vs perennial FLOWERING PLANT REPRODUCTION • ASEXUAL: without sex – Make clones – Little genetic diversity • SEXUAL: with sex – Mix of male and female traits – Great genetic diversity FLOWERING PLANT REPRODUCTION: STEPS IN SEXUAL REPRODUCTION • Gamete Production – Eggs produced in ovary – Sperm produced in anther and packaged two per pollen grain FLOWERING PLANT REPRODUCTION: STEPS IN SEXUAL REPRODUCTION • Pollination – Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma Pollen transferred by wind, water, animals Double Fertilization 2 Polar Nuclei Pollen tube biology.kenyon.edu • The two sperm in each pollen grain go down pollen tube that grows from stigma to ovary. • One sperm fertilizes egg which develops into embryo (becomes new plant). • Other sperm fertilizes two polar nuclei to form endosperm, which supplies energy and nutrients to embryo. FLOWERING PLANT REPRODUCTION: STEPS IN SEXUAL REPRODUCTION • Seed Production – Package embryo and endosperm into seed coat • Seed Dispersal – Movement of seeds away from parent plant – Methods include exploding seed pods, wind, water, animals (eaten, hook on, etc.) Exploding seed pod video www.urbanext.uiuc.edu