* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nonvascular Plants
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
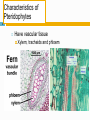
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
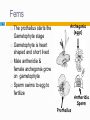
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
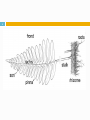
1 SIMPLE VASCULAR PLANTS Pteridophytes (Ferns) 2 Seedless Vascular Plants Divisions 3 Psilophyta – Whisk ferns Lycophyta – Club mosses Sphenophyta – horsetails Pteridophyta - ferns Not for examinations Ferns 4 Largest group of extant (living) vascular plants Wide range of habitats (terrestrial, aquatic, arboreal tree ferns, epiphytic) Can asexually reproduce by Rhizomes (underground stems) Rhizome Ferns 5 Dominant Sporophyte stage has true roots, stems, and leaves Roots and stems underground Leaves called fronds found above ground and attached to a stem like petiole Fronds 6 7 the fiddle head coming off the rhizomes. Parts of the Fern Sporophyte 9 Characteristics of Pteridophytes 10 Have true leaves and roots Leaves are called fronds New leaves are coiled in a bud Characteristics of Pteridophytes 11 Roots are fibrous Anchor the plant And absorb water and minerals Grow out of the rhizome (horizontal stem) that grows partially underground Characteristics of Pteridophytes 12 Have vascular tissue Xylem, tracheids and phloem Characteristics of Pteridophytes 13 Reproduce by means of spores Spore cases called sporangia are found on the underside of sporophylls Sporangia often occur in clusters called sori 14 15 Characteristics of Pteridophytes Wind spreads spores that land on moist soil & germinate into a prothallus (tiny independent gametophyte) that produces gametes Prothallus Ferns 16 The prothallus starts the Gametophyte stage Gametophyte is heart shaped and short lived Male antheridia & female archegonia grow on gametophyte Sperm swims to egg to fertilize Archegonia (eggs) Prothallus Antheridia Sperm Characteristics of pteridophytes 17 Produce motile male gametes Rely on water for fertilisatiom Fern Prothallus with archegonia Fern sperm cell 18 Egg cells are produced in archegonia Fern Archegonia. 19 20 Uses for Ferns EXTRA 21 Help prevent erosion Fiddleheads are eaten as food Ornamental plants for yards and homes Helped form coal deposits millions of years ago 22 THE END