* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download tougher_plants
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Cultivated plant taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Embryophyte wikipedia , lookup
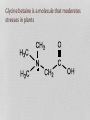
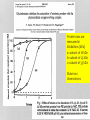
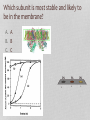
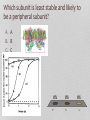
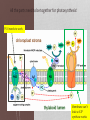
Tougher Plants: Beating Stress by Protecting Photosynthesis in Genetically Modified Plants Based on a case study by R. Pals-Rylaarsdam and M.L. Tischler Department of Biological Science Benedictine University, Lisle, IL Plants are subject to many stresses • The main stressors are: Cold Heat Salt Frost damage Heat damage Road runoff Irrigation evaporation or drought Glycine betaine is a molecule that moderates stresses in plants Plants are subject to many stresses • The main stressors are: Cold Heat Salt Frost damage Heat damage Road runoff Irrigation evaporation or drought Wild type Transgenic Plants were exposed to 3C for 7 days, then transferred to the warm greenhouse. NB: This figure is a simulation of a figure in the original article. What does wild type mean? gt he te r ay in al lly Gr o up di et ic a Ge n 0% gr e. .. ou p ed nc on tr in gu sh ow up Gr o 0% gr ... ta l im en pe r ex re d lte Un a 0% o. .. 0% sp l A. Unaltered experimental group B. Group showing uncontrolled or “wild” grow C. Genetically altered group D. Group displaying the greatest variance in an observed trait What does glycine betaine do for the leaves, flowers and fruits in cold-exposed plants? What does glycine betaine do? Figure 3. Effects of chilling on various growth parameters. Five-week-old greenhouse-grown wild type and independent homozygous transgenic lines (L1, L5) were chilled (3°C) for 5 days, then returned to greenhouse. WT: wild type tomato plants L1-L9: different lines of transgenic plants Which photosynthesis process is most effected by ion leakage? AT P Ca W he t he r th e he r he t W 0% 0% sy nt he ha th se er w el i.. ec tr on sw ill t.. . cle cy lvi n ca n ca ce lls he r he t W 0% ... pt ur e. .. 0% W A. Whether cells can capture light B. Whether the Calvin cycle will function C. Whether ATP synthase will function D. Whether electrons will transfer from PS II Plants are subject to many stresses • The main stressors are: Cold Heat Salt Frost damage Heat damage Road runoff Irrigation evaporation or drought Figure 4. Changes in the oxygenproducing activity of PSII determined with thylakoid membranes isolated from leaves after exposed to different temperatures 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, or 50°C in the chambers for 4 h, in wild type and transgenic plants. The values are mean + SE of three independent experiments. Oxygen-evolving activity of PSII (mmol O2 mg-1 Chl h-1) 400 300 200 100 WT Genetically modified 0 20 25 30 35 40 Temperature of treatment 45 (oC) 50 55 WT: Wild type tobacco plants and genetically modified tobacco plants Which process in photosynthesis produces O2? PS I PS II ATP synthase Light capture 0% 0% pt ur e ca L ig ht AT P sy nt ha s e II 0% PS I 0% PS A. B. C. D. Make two observations from the data Figure 4. Changes in the oxygenproducing activity of PSII determined with thylakoid membranes isolated from leaves after exposed to different temperatures 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, or 50°C in the chambers for 4 h, in wild type and transgenic plants. The values are mean + SE of three independent experiments. Photosystem II Structure of Photosystem II, PDB 2AXT http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:PhotosystemII.PN Which part of the molecule goes through the membrane? A. Blue box B. Red oval d ov al 0% Re Bl ue bo x 0% So, the blue box is trans-membrane. The part below the blue box is associated with the membrane. Structure of Photosystem II, PDB 2AXT http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:PhotosystemII.PN G Which of the following could explain why increased temperatures decrease PSII activity? ... to d tb in pr o te in sl .. an no rc at e W 0% PS I.. . 0% he ra l er ip Th ep hl o ec Th 0% lb re ak s. ro ph yl m em br an es b. .. 0% ko id d. yla b. c. Thylakoid membranes become more permeable to ions The chlorophyll breaks down The peripheral proteins lose their ability to bind to the transmembrane proteins Water cannot bind to PSII to form oxygen Th a. Plants are subject to many stresses • The main stressors are: Cold Heat Salt Frost damage Heat damage Road runoff Irrigation evaporation or drought Protein sizes are measured in kilodaltons (kDa) a: subunit of 18 kDa b: subunit of 23 kDa c: subunit of 33 kDa Make two observations Which subunit is most stable and likely to be in the membrane? A. A B. B C. C 0% A 0% B 0% C Which subunit is least stable and likely to be a peripheral subunit? A. A B. B C. C 0% C 0% B A 0% What does glycine betaine do to protect PSII activity? ot e m Be ta in e pr o e o ha ve .. 0% ap pe rs t ns . .. ra Be ta in pr o e Be ta in 0% sd is s oc . .. 0% te ct st ts p er ip he r.. 0% te c D. pr o C. e B. Betaine protects peripheral proteins again dissociation due to salt Betaine protects transmembrane proteins from dissociation due to salt Betaine promotes dissociation of transmembrane and peripheral proteins in the thylakoids Betaine appers to have no impact on membrane proteins of the thylakoids Be ta in A. All the parts need to be together for photosynthesis! PS II needs to work Membrane can’t leak so ATP synthase works