* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WEATHER
Water vapor wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Air quality law wikipedia , lookup
Severe weather wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Thunderstorm wikipedia , lookup
Automated airport weather station wikipedia , lookup
Lockheed WC-130 wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric circulation wikipedia , lookup
Cold-air damming wikipedia , lookup
Weather lore wikipedia , lookup
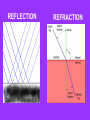
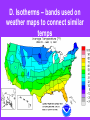
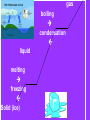
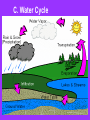
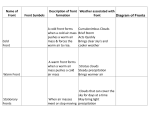
WEATHER Meteorology Study of weather I. Basic Principles A. Earth in space 1. earth – spins on own axis & completes one rotation every 24 hrs. (causing day & night) 2. earth – takes 1 year to complete 1 orbit (revolution) around the sun 3. earth’s axis tilted: 1 hemisphere receives more light causing summer; less light – winter a. equinox – sun directly overhead on equator; - autumnal equinox – Sept. 21 - spring (vernal) equinox – March 21 b.) solstice –when the sun’s overhead on: - Tropic of cancer – summer solstice: June 21st - Tropic of capricorn – winter solstice: Dec. 21st Tilt/Seasons – 0:50 B. Atmosphere - 310 miles 2000 oC or higher -50 miles/ -120 oC -31 miles/ 0 oC -ozone layer - 11 miles/ -80 oC - weather takes place 1. troposphere – lowest region where weather occurs; contains water vapor & clouds; contains 78.08 % (78%) N2 and 20.94% (21%) O2 2. stratosphere – warmer due to ozone (O3) layer; absorbs UV radiation Our Atmosphere – 2:40 C. 3 causes of weather – pressure, temp., precip. II. Pressure - downward force exerted by the weight of the air; greatest at sea level; measured by the weight of the air (barometer) A. Higher pressure has a higher temp.; - less pressure - cooler; ex. mt., heat pump - less pressure – lets air rise faster to make winds B. Wind – air moves from a high to low pressure (H L) Pressure moves from H L C. High pressure systems (H) – move clockwise & generally result in fair weather D. Low pressure systems (L) – move counterclockwise & generally result in unsettled (bad) weather E. Isobars – lines on weather maps to connect similar pressures Air Pressure – 2:11 High/Low Pressure – 1:00 III. Temperature Measure of amt. of energy of the molecules; caused by sun; measured by thermometer A. Sunshine 1. warmth & light 2. photosynthesis – makes food & O2 3. helps in evaporation/transpiration drives the water cycle 4. creates optical effects a. reflection – light bounces off a surface; ex. oceans reflect light - albedo effect – reflectiveness of a surface; ex. snow & white shirt – high albedo b. refraction – light moving from 1 medium to another, causes the speed to change & bends the light; ex. mirage REFLECTION REFRACTION B. Conduction 1. Heat striking an object transfers some energy to object; ex. sand gets hot on feet 2. materials vary in amount of heat absorbed (specific heat capacity) before temp. increases; ex. metal heats up faster than wood C. Density of different temp. 1. heat – less dense, warm air rises 2. cold – more dense, cold air sinks 3. convection current – warm fluid that is less dense & rises; ex. in atmosphere, ocean, under the crust D. Isotherms – bands used on weather maps to connect similar temps Sunlight & Solar Energy – 1:49 E. Temperature Fronts 1. cold front – barometer falls – low; large clouds form; violent storms – thunder & lightning 2. warm front – less violent storms; don’t move as fast but last longer; as warm air rises, it cools & condenses precip. Fronts – 3:17 IV. Water A. Importance? Available B. H2O & the weather – can occur in all 3 states at ordinary temps. gas boiling condensation liquid melting freezing Solid (ice) - takes a great deal of energy to change the temp. - oceans fluctuate less than land - cold/warm ocean currents affect the air temp. above it C. Water Cycle - 9 places water found: clouds, groundwater, oceans, lakes, rivers, soil, plants, animals, glaciers D. Clouds and Fog 1. Relative humidity: 100% - air becomes saturated; fog – ground level; clouds – above ground; warm air holds more moisture than cold air 2. water vapor (normally) condenses only onto a surface; ex. Dust, soot, sulfate the bigger the particle the bigger the droplet; called CCN – cloud condensation nuclei E. Rain water droplets more than .5 mm across collects around CCN; when too heavy they fall as rain F. Snow & Sleet 1. Snow – water freezes to form crystals 2. Sleet – ice pellets smaller than 5 mm in diameter G. Hail, thunder, lightning – caused by rising warm air 1. Hail – rising air currents carry water droplets up & they freeze. This process continues & refreezes in layers. When heavy enough to overcome air currents, they drop 2. Thunder & lightning – rising air currents create convection currents – hot air rises at center while cold air sinks at sides - thundercloud: has + electrical charge at top & - charge at the bottom. Eventually huge sparks flash between the charges, neutralizing them lightning. - Lightning releases so much energy – that air which passes through it explodes thunder - the difference in electrical charge can be more than 305 volts/ft. What are Thunderstorms? – 0:43 How do Thunderstorms form? – 2:41 Updrafts & Hail – 1:10 H. Dew & water Clear skies cause quick cooling, chilling the air next to it. Water vapor condenses on surface dew (dew point reached) THE END!