* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download “Meteorology”? - U. S. Naval Sea Cadet Corps Resources Page
Space weather wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Precipitation wikipedia , lookup
Weather forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Air well (condenser) wikipedia , lookup
Thunderstorm wikipedia , lookup
Marine weather forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric circulation wikipedia , lookup
Severe weather wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Automated airport weather station wikipedia , lookup
Lockheed WC-130 wikipedia , lookup
Cold-air damming wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric convection wikipedia , lookup
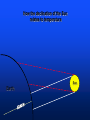
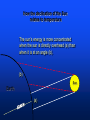
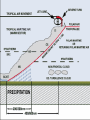
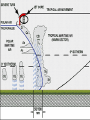
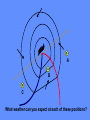
U. S. Naval Sea Cadet Corps Marathon Division BASIC METEOROLOGY © 2004 Marathon Division OBJECTIVES • Teach basic weather terminology • Teach the importance of weather and forecasting • Teach a basic understanding of how the elements of weather interact with each other What is “Meteorology”? The study of weather and the elements of weather Weather Elements TEMPERATURE • Heating of the earth’s atmosphere by the sun • Warm air rises / Cool air sinks • Measured with the thermometer How the declination of the Sun relates to temperature Sun Earth How the declination of the Sun relates to temperature The sun’s energy is more concentrated when the sun is directly overhead (a) than when it is at an angle (b). (b) Sun Earth (a) PRESSURE • Vertical airflow (caused by changes in temperature) which results in LOW and HIGH Pressure areas. • Creates horizontal airflow (wind) • Measured with a Barometer • Isobars - lines of equal pressure Warm Air RISES L Cold Air SINKS H WIND • “Unequal distribution of heat energy in the atmosphere” • Uneven heating of the earth’s surface • Wind speed measured with an Anemometer • Wind direction measured with a Wind Vane (weather vane) WIND (cont.) • Coriolis Effect due to the earth’s rotation about its axis will skew the direction about 15 degrees • Clockwise change - “VEER” • Counterclockwise change - “BACK” CLOUDS • Minute water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the atmosphere • Formed by rising warm air masses • Water vapor condenses forming water droplets • Numerous types found in three layers CLOUDS (cont.) • • • • • Low level - Cumulus Mid level - Prefixed with “alto” High level - Cirrus Cumulonimbus - Thunderstorms Valuable tool in forecasting HUMIDITY & PRECIPIATATION • Rain, snow, sleet, fog • The condensation of water in the atmosphere • Rising air mass cools causing the water vapor to condense into minute droplets. • When the droplets get large (heavy) enough, they fall as rain/snow. HUMIDITY & PRECIPIATATION (cont.) • What is a desert? • If the equator is the warmest region on earth, why aren’t deserts found there? • What is the largest desert on earth? FRONTS • WARM - red line or half circles • COLD - blue line or points • OCCLUDED - purple or both symbols on the same side • STATIONARY - half circles on one side, points on the other WARM FRONT WARM AIR COOLER AIR Warm Front • • • • • • Increasing clouds out to 600 miles Decreasing cloud ceiling Steady rain within 200 miles of front Barometer dropping Wind generally out of the southeast Expect rain and bad weather within 48 hours PRECIPITATION Passing of Warm Front • Intense or heavy rain diminishes and weather improves • Partly Cloudy sky • Wind shift to the Southwest • Barometer steady or slightly rising COLD FRONT WARM AIR COLD AIR Passage of Cold Front • • • • Cumulonimbus clouds Weather deteriorates rapidly Thunderstorms Wind shift to the NW with passage of the front • Weather improves rapidly with rising barometer OCCLUDED FRONT WARM AIR COLD AIR COOL AIR A B C What weather can you expect at each of these positions?