* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Patches - carmelacanzonieri.com
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
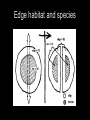
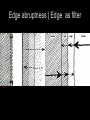
Landscape mosaic Patch types Desert vegetation Desert vegetation Esker 1 Esker 2 Kettle Mesa Verde fire map Mesa Verde satellite Compare Fire patch Animals trampling Wind patterns mudslides Alluvial fan Alluvial Fan Strip mining Human pattern plantation Orchards Logging Logging PATCH SHAPE Patch shape determines the distance between the patch’s edge and the patch’s habitat interior, and the core area • Compact forms are effective in protecting their internal resources against negative effects of the surroundings • Convoluted forms are effective in enhancing interactions with the surroundings. A long common boundary provides a greater probability of movements across • A compact patch contains higher species richness than an elongated patch that has fewer interior species • Interior area adds species at a greater rate than increasing edge area Convoluted patches have a long perimeter and abundant exchanges with the matrix. A convoluted patch causes complex patterns of turbulence in water and wind flow. Most turbulence will be on the outside of a-remnant patch, and the inside of a disturbance patch The turbulence may create considerable microheterogeneity in soil,water,vegetation, and fauna surrounding a remnant patch BOUNDARIES AND ECOTONES Sharp boundaries from human activities Gradual ecotones in natural landscapes Edge habitat and species • Large patches contain interior conditions that foster interior species absent in small patches • Edge width varies according to wind direction, sun direction, and internal edge structure Edge width Edge abruptness | Edge as filter PATCH CONFIGURATION AND CONTEXT The distance between patches and the characteristics of the context influence species Consider the contribution of patches to the landscape structure • The orientation of the long axis of the patch is key to several ecological processes From Forman 1995 • Population Viability Analysis PVA is used to determine the size of populations needed for long term survival. It takes into account environmental, demographic and genetic variables that determine extintion probabilities for each species • Minimum patch area is the smallest patch needed to sustain specific species or ecosystem functions Appendix B in the ELI document ex. Bear 900ha, grizzly 2800, cougar 220.000 rodents, rabbits 1 to 10ha Protection of habitat patches of 55ha appears to capture 75% of species requirement in the ELI survey. This will not capture particularly area-sensitive species