* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download food chain
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
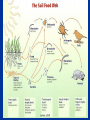
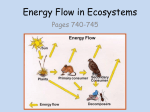
Ecosystems Food Chains/Webs, Energy Pyramids, Symbiotic Relationships Predatory-Prey Interaction, & Competitions James, 2009 Ecology Study of how organisms INTERACT with each other and their environment. James, 2009 Life Levels and Organization James, 2009 Biosphere • The biosphere is the outermost part of the planet’s shell — including air, land, surface rocks, and water — within which life occurs, and which biotic processes in turn alter or transform. James, 2009 Biome • A biome is a major regional group of distinctive plant and animal communities best adapted to the region's physical natural environment, latitude, elevation, and terrain. • Examples of biomes include the desert, rain forest, arctic tundra, grassland, coniferous forest, deciduous forest, and oceans. James, 2009 Coral Reef Ecosystems James, 2009 Yellowstone National Park Ecosystem James, 2009 Ecosystems • All the biotic (living) and abiotic (nonliving) factors that will INTERACT with each other in some subset of the biosphere. • Abiotic factors: soil, water, temperature, elevation, and location on the earth. James, 2009 Explain • Community – – Groups of many different species of organisms interacting in a particular area (predator prey relationships) Only the biotic factors that interact between different species of organisms • Population – A group of organisms of ONE species that interbreed and live in the same place at the same time. James, 2009 Producer (autotroph) • Producers (autotrophs) are always at the base of the chain. Producers are organisms that make their own food. Plants are producers. James, 2009 Herbivore • Herbivores are animals that only eat plants. • Ex. Cow & deer James, 2009 Omnivore • An omnivore eats both plants and animals. • Ex. Humans & bears James, 2009 Carnivore • Animals that eat meat are carnivores. • Ex. Lion & wolf James, 2009 Decomposer • A decomposer eats dead or dying organisms. James, 2009 Producers and Consumers • So…producers make their own food (e.g., photosynthesis) and consumers don’t. • Is a dog a producer or a consumer? • Is a termite a producer or a consumer? James, 2009 Food Chain • A food chain shows how the energy in food is passed from one organism to another in an ecosystem. James, 2009 Describe the Food Chain James, 2009 Describe the Food Chain James, 2009 Food Webs • Many food chains interacting with each other. • The arrow always points away from the organism being eaten to the organism doing the eating. • Shows the movement of energy and matter in an ecosystem. James, 2009 James, 2009 Energy Pyramid • Sun major supplier of the earth’s energy. • Most of the energy released is lost in the form of heat. James, 2009 The Flow of Energy • Producers - Plants capture the sun’s energy and store it in food • Primary Consumers (herbivores) - Animals that receive their energy directly from plants • Secondary Consumers (carnivores) Consumers that feed on primary consumers • Energy flows from the sun to the producer, then to the primary consumer, then to the secondary consumer, third level consumers, forth level consumers, etc... James, 2009 Pyramid of Numbers • Carnivore populations are smaller in comparison to the rest of the ecosystem. • They require more food to sustain their lives than the lower organisms. • The amount of usable energy that is transferred from trophic level to trophic level only 10%. James, 2009 Explain • Competition for limited food, water, and space resources, which results in some organisms not being able to get enough resources for survival • Predator-prey interaction occur when a predator captures and eats prey for food. • Symbiosis which are long-term, close relationships between species. James, 2009 Symbiotic Relationships • Mutualism is a relationship in which both species mutually benefit. • Commensalism is a relationship in which one species benefits while the other species is affected. • Parasitism is a relationship in which one species benefits while the other is harmed. James, 2009 PowerPoint information provided by Xtreem Science at www.coe.unt.edu/tegs and Gateway to Science – Grade 8 Created By: Makayla James McCowan Middle School James, 2009