* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Importance of Biodiversity
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Conservation biology wikipedia , lookup
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
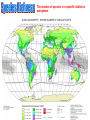
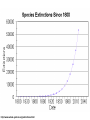
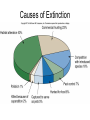
INTRODUTION • “From the driest desert to the dripping rainforests, from the highest mountain peaks to the deepest ocean trenches, life on earth occurs in a marvelous spectrum of sizes, colors, shapes, life cycles, and interrelationships. Think for a moment how remarkable, varied, abundant, and important the other living creatures are with whom we share this planet. How will our lives be impoverished if this biological diversity Cunningham, 2003 diminishes?” Cunningham, 2003 “Biodiversity refers to the varieties of organisms and complex ecological relationships that give the biosphere its unique, productive characteristics” The number of species in a specific habitat or ecosystem Global Biodiversity Patterns and Processes as you move southward from the North Pole (or northward from the South Pole) – Global biodiversity increases Functional Diversity The biological and chemical processes such as energy flow and matter recycling needed for the survival of species, communities, and ecosystems. Genetic Diversity The variety of genetic material within a species or a population. Ecological Diversity The variety of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems found in an area or on the earth. Species Diversity The number and abundance of species present in different communities Fig. 3-12, p. 48 http://www.whole-systems.org/extinctions.html Recent extinctions, endangered or threatened species in North America, including Canada, go to: http://www.currentresults.com/Endangered-Animals/North-America/recentlyextinct-animals.php the loss of a species from the Earth. a species that no longer lives in the wild in a specific area but lives elsewhere. a species that are in imminent danger of going extinct or becoming extirpated. a species that is likely to become endangered if current trends and conditions continue. a species that may become threatened or endangered because of a combination of factors Hinterland Who’s Who – Species at Risk Canada's (all categories above) Species Causes of Extinction Benefits of Biodiversity • • • • • • Food and drink Medicines Industrial materials Ecological services Leisurely, cultural, and aesthetic values Causes of Biodiversity Loss • • • • • • • • Pollution Loss of tropical forest Spread of urban areas Warfare Large dam construction Road building Tourism Loss of traditional lifestyles Consequences of Biodiversity Loss • • • • • Loss of food Decrease in biomass Collapse of food web Loss of keystone species Reduction of ecosystem efficiency and community productivity • Loss of medicinal supplies • Increased vulnerability of species to disease and predation Click on above or go to: http://www.biodiversityislife.net/