* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Human population planning wikipedia , lookup
Maximum sustainable yield wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
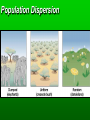
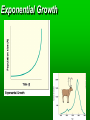
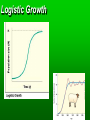
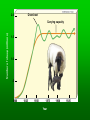
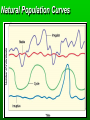
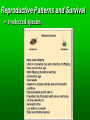
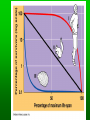
Population Ecology Key Concepts Factors affecting population size Species reproductive patterns Species survivorship patterns Conservation biology and human impacts on ecosystems Population Dynamics and Carrying Capacity Population dynamics Biotic potential (intrinsic rate of increase [r]) Environmental resistance Carrying capacity Exponential and Logistic Growth Population Density Sampling Populations • • • • • Direct Count Point Sampling Transect Sampling Quadrat Sampling Mark and Recapture Population Dispersion Factors Affecting Population Size Exponential Growth Logistic Growth Environmental resistance Population size (N) Carrying capacity (K) Biotic potential Exponential growth Time (t) Population overshoots carrying capacity Number of reindeer 2,000 Population crashes 1,500 1,000 500 Carrying capacity 1910 1920 1930 Year 1940 1950 2.0 Overshoot Number of sheep (millions) Carrying capacity 1.5 1.0 .5 1800 1825 1850 1875 Year 1900 1925 Capture-recapture method interaction. Click to view animation. Population Density Effects Density-independent controls Density-dependent controls Natural Population Curves The Role of Predation in Controlling Population Size Predator-prey cycles Top-down control Bottom-up control Reproductive Patterns and Survival Asexual reproduction Sexual reproduction Reproductive Patterns and Survival r-selected species Reproductive Patterns and Survival K-selected species Carrying capacity K Number of individuals K species; experience K selection r species; experience r selection Time Survivorship Curves Survivorship Curves. Click to view animation. Human Impacts on Ecosystems Habitat degradation fragmentation Introduction of non-native species Pollution Population explosion of humans Overharvesting renewable resources Human Impacts on Ecosystems Ecosystem simplification Genetic resistance Predator elimination Interference with ecological systems Learning from Nature Dependence on Nature Interdependence Unpredictability Limited resources Recycle wastes Solutions Principles of Sustainability How Nature Works Lessons for Us Runs on renewable solar energy. Rely mostly on renewable solar energy. Recycles nutrients and wastes. There is little waste in nature. Prevent and reduce pollution and recycle and reuse resources. Uses biodiversity to maintain itself and adapt to new environmental conditions. Preserve biodiversity by protecting ecosystem services and preventing premature extinction of species. Controls a species population size and resource use by interactions with its environment and other species. Reduce births and wasteful resource use to prevent environmental overload and depletion and degradation of resources. Property Natural Systems Human-Dominated Systems Complexity Biologically diverse Biologically simplified Energy source Renewable solar energy Mostly nonrenewable fossil fuel energy Waste production Little, if any High Nutrients Recycled Often lost of wasted Net primary productivity Shared among many Used, destroyed, or species degraded to support human activities