* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download physics powerpoint review 1st
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
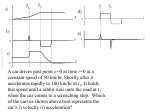
Chapter 1 • Introduction Pg 13 Chapter 2 Measurement •Metric System Accuracy and Precision •Scientific Notation Absolute and Relative Error •Significant Figures Graphing Data •Power Relation y = ax2 •Direct Variation y = mx + b •Inverse Variation y = k/x •Solving Equations •Dimensional Analysis •Review Pg 37-38 Chapter 3 •Kinematics •Speed •Time •Velocity •Acceleration •Review Motion Pg 60-61 Chapter 4 Vectors •Adding Graphically •Head-Tail, Parallelogram Method •Adding Mathematically •Pythagorean Theorem, SOHCAHTOA •c2 = a2 + b2 Tan = y/x •c2 = a2 + b2 - 2ab cos C •sin A/a = sin B/b = sin C/c •Review Pg 77-78 Chapter 5 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Graphical Analysis Distance-Time Graph Speed-Time Graph Acceleration-Time Graph Distance-Time Graph Speed-Time Graph Acceleration-Time Graph Constant Speed Constant Speed Constant Speed Uniform Acceleration Uniform Acceleration Uniform Acceleration d d1 d0 v t t1 t 0 v v1 v0 a d d0 vt t t1 t 0 1 2 d d0 at 2 v2 v 0 2 2ad v v0 at Review Pg 107-108 Chapter 6 Forces •Types of Force Friction Terminal Velocity •Newton's Laws Falling Bodies Air Resistance •Mass vs Weight F = ma Pendulum •Ff=µFN l T 2 g Review Pg 144-145 Chapter 7 Forces in Two Dimensions •Equilibrium, Equilibrant •Motion in Two Dimensions •Projectile Motion •Centripetal Force •Simple Harmonic Motion •Review Pg 169-170 v a r 2 2r v , t Fr T Chapter 8 Gravity TA rA TB rB 2 •Kepler's Laws •Universal Gravitation •Inverse Square Law •Escape Velocity •Review Pg 193-194 3 mAm B F G 2 d r3 T 2 GmE F g m Chapter 9 Momentum •Impulse-Momentum •p = m v f t = m v •Conservation of Momentum •m1v1 + m2v2 = m1v1' + m2v2' •Elastic and Inelastic Collisions •Review Pg 217-218 Chapter 10 Work •Work •Power •Net Force •Types of Machines •IMA, AMA, efficiency •Rotation and Torque •Angular Momentum •Review Pg 241-242 w = Fd w = F (cos ) d w P t Fr MA Fe de IMA dr WO eff x 100 % Wi MA eff x 100 % IMA Chapter 11 Energy •Potential Energy •Kinetic Energy •Conservation of Energy •Review Pg 267-268 PE mgh 1 2 KE mv 2 1 Simplify using significant digits a. 8.24 - 3.159 5.08 b. 131 x 21.23 c. 12 - 3.12 d. .012 + 3.21 2.78 x 103 9 3.22 2. Convert a. 2.3 mm = ? km 2.3 x 10-6 km b. 2.1 m/s = ? km/hr 7.56 km/hr c. 3 kg = ? mg 3 x 106 mg d. 4.5 ml = ? L .0045 l 3. A car goes from 36 m/s to 15 m/s in 3 sec. What is the acceleration and the distance traveled? a d v f vi t 15 36 7 m/s 2 3 (vi v f )t 2 (36 m/s 15 m/s) (3s) 76.5 m 2 4. Police measure skid marks 60 m long. The acceleration for dry pavement is -10 m/s2. Was the car exceeding the 80 km/hr speed limit? How long did it take to stop once the brakes were applied? v 2f vi2 2ad 0 v12 2(10 m/s 2 )(60 m) vi2 1200 vf = vi = at Yes vi 34 m/s 124 km/hr 0 = (34 m/s) + (-10 m/s2)(t) 5. Use the graph at the right to answer the following questions. a. How far does the object go between 5 and 6 seconds? 6m b. What is the acceleration between 8 and 9 seconds? -1 m/s2 c. What is the total distance traveled? 35 m (total area under the curve) d. When is the acceleration the greatest? Between 3-4 seconds (Slope is the steepest) 6. An object with a mass of 20 kg is accelerated upward with a force of 400 N. a. What is the weight of the object? W = mg W = (20)(9.8) = 196 N down b. What is the net force? 400N – 196 N = 204 N up c. What is the acceleration of the object? a = F/m = 204/20 = 10 m/s2 up 7. A force of 7 N at 90 is added to a force of 12 N at 180. Find the resultant and the equilibrant. R2 = a2 + b2 = 72 + 122 = 193 R = 13.6 N E = 13.6 N @ 60° East of South = tan-1(7/12) = 30° R = 13.6 N @ 60° West of North 8. A trunk weighing 230 N is begins to slide down an incline with an angle of 30. Find the magnitudes of the parallel and perpendicular components and the coefficient of friction. Fx = F sin = 230 sin (30°) = 115 N Fy= F cos = 230 cos (30°) = 199 N µ = Fx/FY = 115N /199 N = tan 30° = .58 30 230 N 30 9. A projectile is fired horizontally with an initial velocity of 34 m/s. Find the range and time in the air. The initial height is 2 meters. t 2d (2)(2m) .64s 2 g 9.8 m/s range = vt = (34)(.64) = 21.72 m 10. A projectile is fired from ground level at an angle of 30 and a velocity of 40 m/s. Find the time in the air, the maximum height, and the range. Sketch the graph. Vx= V cos = 40 cos (30°) = 34 m/s Vy= V sin = 40 sin (30°) = 20 m/s t v f vi a 20 m/s 20 m/s 4.1 s 2 9.8 m/s 1 2 d vi t at (20 m/s)(2.05 s) (4.9 m/s 2 )(2.05 s) 2 20.4 m 2 d vt (34 m/s)(4.1 s) 139 m 11. An object with a mass of 2 kg is attached to a string with a length of 2.5 m. Find the speed of the mass, the acceleration, and the centripetal force on the object. The frequency is 2 cycles per second. v 2r (2 )(2.5 m) 31.4 m/s T .5 s v 2 (31.4 m/s) 2 ac 394.46 m/s 2 r 2.5 m Fc mac (2kg)(394.4 6 m/s 2 ) 788.8 N 12. Find the period of a pendulum with a length of 1.4 meters. T 2 l 1.4 m 2 2.37 s 2 g 9.8 m/s 13. Two masses of 3 kg and 8 kg respectively are separated by 1.2 m. Find the force of attraction between them. 2 m1m2 11 N m (3 kg)(8 kg) F G 2 6.67 x10 1.11 x 10 9 N 2 2 d kg (1.2m) 14. A car weighing 16,000 N moving at 15 m/s is acted upon by a 700 N force until it is brought to a halt. Find the car's mass, the initial momentum, and how long it takes for the car to stop. m t W 16000N 1632kg 2 g 9.8m/s mv 24489 kg m/s 34.9s F 700N p mv (1632 kg)(15 s) 24489 kg m/s 15. A 35 g bullet moving at 460 m/s strikes a 10 kg block of wood. The bullet becomes imbedded into the block. How fast is the bullet and block going after the collision? pbefore = pafter (.035 kg)(460 m/s) + (10 kg)(0 m/s) = (10.035 kg) v 16.1 kg m/s = (10.035 kg) v v = 1.6 m/s 16. A lawnmower is pushed with a distance of 10 meters with a force of 60 N at an angle of 40 for 2 minutes. Find the net force, work done, and the power generated. Fnet F cos (60)(cos 40 ) 45.96 N W Fnet d (45.96 N)(10 m) 459.6 J W 459.6 J P 3.83 W t 120 s 17. A worker uses a pulley system to raise a 25 kg box 16.5 m. A force of 129 N is exerted and the rope is pulled 33 m. Fins the mechanical advantage, ideal mechanical advantage and the efficiency. FR (25 kg)(9.8 m/s 2 ) MA 1.9 FE 129N d E 16.5 m IMA 2 dR 33 m eff MA 1.9 x 100% x 100% 95% IMA 2 18. A 20 kg object is at a height of 20 m. Find the potential energy. PE mgh (20 kg)(9.8 m/s 2 )(20 m) 3920 J 19. An object has a mass of 34 kg and is moving at 13 m/s. Find the kinetic energy. KE 1 2 1 mv (34 kg)(13 m/s) 2 2873.5 J 2 2 TF TF TF 11. The SI unit of work is called the joule. 12. The rate at which work is done is called energy. 13. When an object is balanced so that any displacement lowers its center of gravity, the object is said to be in stable equilibrium. T F 14. There is a force on the earth that is directed toward the sun. T F 15. When the earth's shadow falls on the moon, a lunar eclipse occurs. T F 16. Ocean tides are caused by differences in the gravitational pull between the Moon and the opposite sides of the earth. T F 17. A bug on a turning record will make more turns per minute if it walks toward the center of the record. T F 18. Ladybugs on the inside of a spinning bicycle tire will experience a force that feels like gravity to them. T F 19. In order to increase his or her rotational inertia, a tightrope walker can carry a long stick. TF TF TF 11. The SI unit of work is called the joule. 12. The rate at which work is done is called energy. 13. When an object is balanced so that any displacement lowers its center of gravity, the object is said to be in stable equilibrium. T F 14. There is a force on the earth that is directed toward the sun. T F 15. When the earth's shadow falls on the moon, a lunar eclipse occurs. T F 16. Ocean tides are caused by differences in the gravitational pull between the Moon and the opposite sides of the earth. T F 17. A bug on a turning record will make more turns per minute if it walks toward the center of the record. T F 18. Ladybugs on the inside of a spinning bicycle tire will experience a force that feels like gravity to them. T F 19. In order to increase his or her rotational inertia, a tightrope walker can carry a long stick. TF TF TF TF TF TF TF TF TF TF 1. 2. 3. 4. The rate at which velocity changes with time is called acceleration. When a car rounds a comer at a constant speed, its acceleration is zero. As a ball falls freely, the distance it falls each second is the same. If you slide a hockey puck across a frictionless ice rink, there must be a horizontal force on the puck to keep it in motion. 5. Excluding the force due to air pressure, there is only one force acting on a book lying at rest on a tabletop. 6. If a bicycle and a parked car have a head-on collision, the force of impact is greater on the bicycle. 7. A quantity that has both magnitude and direction is called a scalar. 8. When all forces acting on an object are balanced, the object is said to be in equilibrium. 9. Momentum is defined as an object's mass times its velocity. 10. The reason a baseball player follows through when hitting the ball is to be in contact with the ball for as long a time as possible. 26. Suppose a car is moving in a straight line and steadily increases its speed. It moves from 35 km/h to 40 km/h in the first second and from 40 km/h to 45 km/h in the next second. What is the car's acceleration? a. 5 km/h/s 27. c. 35 km/h/s d. 40 km/h/s A ball is thrown straight up. At the top of its path, its instantaneous speed is a. 0 m/s. 28. b. 10 km/h/s b. about 5 m/s. c. about 10 m/s. d. about 20 m/s. The law of inertia states that an object a. at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an outside force. b. will continue moving at the same velocity unless an outside force acts on it. c. will continue moving in a straight line unless an outside force acts on it. d. All of the above 29. How much force is needed to accelerate a 2-kg physics book from rest to a speed of 6 m/s in 1 second? a. 36 N b. 12 N c. 3 N d. 0.33 N 30. Friction is a force that always acts a. in a direction opposite to the direction of an object's motion. b. in the same direction as the object’s motion. c. in a direction perpendicular to the object's motion. 31. If a horse pulls on a wagon at rest, the wagon pulls back equally as much on the horse. Will the wagon be set into motion? a. b. c. d. No, because the forces cancel each other. Yes, because there is a net force acting on the wagon. Yes, because there is a time delay between action and reaction. Yes, because the horse's pull on the wagon is greater than the wagon's pull on the horse 32. A cannonball is fired at some angle into the air. In the first second, it moves 10 meters horizontally. Assuming it does not hit the ground and air resistance is small, how far will the cannonball move horizontally in the next second? a. More than 10 m b. 10 m c. Less than 10 m d. There is not enough information to say. 33. The reason padded dashboards are used in cars is that they a. increase the force of impact in a collision. b. increase the time of impact in a collision. c. decrease the momentum of a collision. d. decrease the impulse in a collision. 34. F= ma is Newton’s ________ Law. a. 1st b. 2nd c. 3rd 35. If you lift one load up two stories, how much work do you do compared to lifting the same load up only one story? a. Four times as much b. Twice as much c. The same amount d. One half as much 36. How much power is required to do 200 J of work on an object in 2 seconds? a. 400 W b. 200 W c. 100 W d. 2W 37. Kinetic energy is the energy an object has because of its a. speed. b. location. c. size. d. temperature. 38. Compared to a car traveling at 50 km/s, how much farther will the same car skid when it is traveling at 100 km/s? a. Five times as far c. Twice as far b. Four times as far d. The same distance 39. If you try to touch your toes while standing flat against a wall, you will probably fall over. This is because a. b. c. d. your center of gravity is outside your support area. your feet extend only a short distance. your center of gravity extends beyond your feet. All of the above 40. The gravitational force between two masses a. is always an attraction. b. depends on how large the masses are. c. depends inversely on the square of the distances between the masses. d. All of the above 41. You can tell if a gravitational force exists in a region of space if a. you let go of a ball and it starts to move. b. you disturb a pendulum and it starts swinging. c. you can weigh yourself. d. All of the above 42. What remains constant for a satellite in an elliptical orbit? a. Its speed c. Its potential energy b. Its kinetic energy d. Its total energy 43. Where does the pickup needle on a phonograph move the fastest across the record? a. At the end of the record b. At the beginning of the record c. Everywhere, because it has the same speed everywhere on the record 44. A car travels in a circle with constant speed. The net force on the car a. is directed forward, in the direction of travel. b. is directed toward the center of the curve. c. is zero because the car is not accelerating. d. None of the above 45. The reason an ice skater turns faster when he pulls his hands in is that a. angular momentum must be conserved. b. there are no large unbalanced torques acting on him. c. his rotational inertia changes. d. All of the above 46. Density is defined as a. mass divided by volume. b. mass times acceleration. c. length divided by time. d. length divided by volume.