* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Harmonic Motion
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
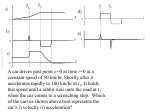
Harmonic Motion Vector Components Circular motion can be described by components. • x = r cos q • y = r sin q For uniform circular motion the angle is related to the angular velocity. • q=wt The motion can be described as a function of time. • x = r cos wt • y = r sin wt r sin q r q r cos q Velocity Components v The velocity vector can also be described by components. • vx = -v sin q • vy = v cos q q v cos q -v sin q q This is the derivative of the position. dx d (r cos wt ) rw sin wt dt dt dy d vy (r sin wt ) rw cos wt dt dt vx Acceleration Components -a cos q q a q For uniform circular motion the acceleration vector points inward. • ax = -a cos q • ay = -a sin q -a sin q This is the derivative of the velocity. dvx d (rw sin wt ) rw 2 cos wt dt dt dv y d ay (rw cos wt ) rw 2 sin wt dt dt ax Changing Angle to Position If only one component is viewed the motion is sinusoidal in time. This is called harmonic motion. Springs and pendulums also have harmonic motion. 1 period x = A cos wt Acceleration and Position In uniform circular motion acceleration is opposite to the position from the center . In harmonic motion the acceleration is also opposite to the position. a x rw 2 cos wt w 2 x This is true for all small oscillations Spring Oscilations From the law of action the force is proportional to the acceleration. F max mw 2 x Harmonic motion has a position-dependent force. • Force is negative • Restoring force F kx mw 2 x w k/m Springboard Find the spring constant from the mass and frequency. w 2f k / m w 2 4 2 f k 4 2 f 2 m A diving board oscillates with a frequency of 5.0 cycles per second with a person of mass 70. kg. What is the spring constant of the board? With values: • k = 42(5.0 /s)2(70. kg) • K = 6.9 x 104 N/m next 2