* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download document
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
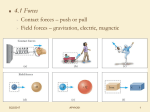
Reading Quiz Review • Choose the correct response: According to Newton's Third Law • If you push on a chair, the chair must push back on you." • "The sum of all forces on an object must be zero." • "Accelerations are caused by forces." • "None of the above." Question 3: Consider a heavy, 16 pound bowling ball at rest with a string tied to it, and the string is pulled with a constant force for one second, causing the ball to move across a nearly frictionless floor. Repeat this experiment with an 8 pound bowling ball, using the same force also for one second. After one second, A. both balls have the same acceleration. B. both have the same velocity. C. the lighter ball has a larger velocity and larger acceleration. D. the heavier ball has a larger velocity and a larger acceleration. E. (None of the above). PHYS 214-First Exam A. First Exam is on Wednesday, February 4. It will cover Chapters 1,2,3, & 4. B. Memorize Newton’s Laws C. Previous exam questions are on the Class Web Site. D. Exam in Room 112 ONLY! Newton’s Third Law • For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. • (memorize) Newton’s Third Law Figure 4.10 The chair pushes back on the hand with a force F2 that is equal in size but opposite in direction to the force F1 exerted by the hand on the chair. Figure 4.11 Two forces, N and W, act on a book resting on a table. The third-law reaction forces –N and –W act on different objects, the table and the earth. Newton’s Laws • Force equals the motion • F = ma (Vector Equation) True in Each of 3 dimensions F ma Figure 4.6 A block being pulled across a table. Two horizontal forces are involved. What is a Newton, our unit of force? What is the acceleration of the block? Figure 4.4 Newton’s first law: In the absence of a force, an object remains at rest or moves with a constant velocity. Newton’s Second Law: The acceleration of an object • is directly proportional to the magnitude of the total force on it, and a F • is inversely proportional to the mass (or inertia) of the object. a 1m Hence, F ma One Newton is the force required to make a 1 kg mass accelerate at 1 meter/sec/sec. How much does a 1 kg mass weigh? Weight=gravitational force= mass times g = mg = (1.0 kg)(9.8m/s2) = 9.8 N = 2.2 pounds Thus we say, incorrectly, “a kilogram is 2.2 pounds”. Note: kilogram is a unit of MASS, pound is a unit of FORCE (=ma). We can also say, correctly, that 1 pound = 4.45 N. Note: Weight depends on value of gravity. Mass is independent of gravity. mass = inertia weight = Force (kilograms) (Newtons) Your weight changes if you go to the Moon. Your mass stays the same. LECTURE QUIZ: Question 1 You are an astronaut floating around on the space shuttle, feeling “weightless”. You need to move a massive box, one that weighed over 200 kilograms on Earth, but now is also floating about the cabin. How much force in Newtons will it take to get the box accelerating at 0.1m/sec^2? 1. 1 newton. 2. 10 newton 3. 20 newton 4. 200 newton 5. The same as on earth LECTURE QUIZ: Question 2 • In the last problem the force required to move the box is equal to lifting a xxx kilogram wt.? • 1 kilogram • 2 kilogram • 10 kilogram • 200 kilogram • The same as in outer space LECTURE QUIZ - Question 3: The Moon is in a circular orbit about the Earth, with a period of about 28 days. A. The Moon is continuously accelerating towards the Earth. B. The Moon never falls and crashes into the Earth because no force is pushing or pulling it towards the Earth. C. The Moon does not fall to Earth because the forces acting on the Earth add up to zero. (They cancel out.) Choose the CORRECT answer. Newton’s First Law • An Object remains at rest, or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted on by an external force. (memorize) Newton’s Second Law • The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the the imposed force. The proportionally constant is the mass of the object. (memorize)