* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download net force
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
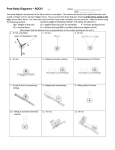
Acceleration depends on both mass and the net force Newton’s 2nd law: The acceleration produced by a net force on a body is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force. It is in the same direction as the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the body. Acceleration depends on both mass and the net force F a m F m a F ma If the net force is zero, there is no acceleration If the net force is not zero, there is acceleration Acceleration depends on net force • A force of 10N accelerates the box Acceleration depends on net force • A force of 20N accelerates the box twice as fast Acceleration depends on mass • A force of 10N accelerates the box Acceleration depends on mass • A force of 10N accelerates the smaller box faster • An airplane weighs 2,000,000N and needs to accelerate at 4m/s2. What thrust (force) must the engines produce? • A train engine has a mass of 120,000kg and pulls a 75,000kg car. The train can pull with a force of 585,000N. What is its maximum acceleration? • Now suppose a second car is added to the train in the last problem. What is the new maximum acceleration? • A train engine mass = 120,000kg • Train car1 = 75,000kg. • Train car2 = 75,000kg. In order for sink a ship in the harbor, a cannon ball of 25kg must be accelerated at 44m/s2. How much force is required to hit the ship? • A stunt penguin want to fly around the room and needs to accelerate enough to compensate for gravity. • If his thruster can produce 88N of force, what is the maximum mass of the penguin and his thruster? Friction • Friction is a force like any other force • Friction acts on materials that are in contact with each other • Friction slows down motion • Forces due to friction are always in the opposite direction of the motion. Find the net force 5N 5N 5N 5N 5N 10N 5N 5N 10N 10N 15N 5N 10N 0N 15N 5N 10N 5N Free-body diagrams Draw the free-body diagram for a book is at rest on a table top. A girl is suspended motionless from a bar which hangs from the ceiling by two ropes. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this: An egg is free-falling from a nest in a tree. Neglect air resistance. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this: A rightward force is applied to a book in order to move it across a desk at constant velocity. Consider frictional forces. Neglect air resistance. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this: A college student rests a backpack upon his shoulder. The pack is suspended motionless by one strap from one shoulder. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this: A skydiver is descending with a constant velocity. Consider air resistance. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this: A force is applied to the right to drag a sled across loosely-packed snow with a rightward acceleration. A free-boy diagram for this situation looks like this A football is moving upwards towards its peak after having been booted by the punter. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this: A car is coasting to the right and slowing down. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this: Net Force • If there is no movement –The net force is zero • If there is no acceleration –The net force is zero • If there is acceleration –The net force is not zero. Free Body diagrams • If the net forces are zero, the FBD is balanced Examples of zero net force? • A book on a desk • A sky diver with a parachute open • A bike moving at a constant speed. Free Body diagrams • If the net forces are NOT zero, the FBD is NOT balanced Free Body diagrams • If the net forces are NOT zero, the FBD is NOT balanced Fnorm Fapp Ffric Fw Examples of non zero net force • A book sliding across a desk • A sky diver falling without a parachute Pressure • P pressure (units are pascals Pa) • P = F/A • A Area • F Force Pressure Hydraulic Pressure Pressure • Does a book’s weight change depending on the angle it is held at? • No W=mg • Does the pressure exerted by a book change depending on the angle it is held at? • Yes Pressure • What is the difference between weight and pressure? • Weight is measured in N • Pressure is N / Area • P=F/A