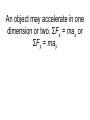* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Physics C IB
Pioneer anomaly wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's law of universal gravitation wikipedia , lookup
AP Physics C I.B Newton’s Laws of Motion The “natural state” of an object Newton’s First Law – If no force acts on a body, the velocity of the body does not change. That is, there is no acceleration Specifically, the net force is zero in the first law. Newton’s Second Law An object may accelerate in one dimension or two. ΣFx = max or ΣFy = may Ex. Three cases for a 0.20 kg hockey puck on a frictionless surface. Find the horizontal acceleration when a) F1 = 4.0 N b) F2 = 2.0 N and F3 = 1.0 N at 30.0º below the horizontal. Ex. Find F3 which will create an acceleration of 3.0 m/s2 in the direction shown. Ex. Three students pull on a ring with the forces shown. The ring doesn’t move. What is the magnitude and direction of FB? Weight and Mass The normal force Tension Newton’s Third Law – When two bodies interact, the forces are always equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. This is true whether the objects are stationary, moving at a constant velocity or accelerating. Ex. For the system of blocks shown a) draw a free body diagram on each block b) find the acceleration of the hanging block c) and the tension in the rope. Ex. For the hanging block shown, find the tension in each rope. Ex. For the block shown find a) the tension in the rope and b) the normal force on the block. Ex. Apparent weight of a 72 kg person in an elevator given by the scale reading (normal force). Find the apparent weight when a) the elevator is at rest or moving at a constant velocity b) accelerating upward at 3.20 m/s2 and c) accelerating downward at 3.20 m/s2. Ex. For the blocks shown find a) the acceleration of the blocks and b) the force on block B by block A. Friction – the book on the table • The book is pushed and released • The book is pushed across the table at a constant velocity • Pushing a stack of books Free body diagrams Love-hate relationship with friction The direction of friction Causes of friction and a couple of equations Ex. In 1960, the longest recorded skid marks (290 m) on a public road, the MI highway in England, were made by a Jaguar. How fast was the car moving at the moment it began skidding? Ex. A woman uses a rope to pull a loaded sled with a mass of 75 kg along a horizontal patch of ice at a constant velocity. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the sled runners and ice is 0.10 and the rope makes an angle of 42º with the horizontal. What is the tension in the rope? Ex. A coin rests on a book. When the book makes an angle of 13º with the table, the coin just begins to slip. What is the maximum coefficient of static friction between the coin and book?