* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Motion
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Inertial frame of reference wikipedia , lookup
N-body problem wikipedia , lookup
Brownian motion wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
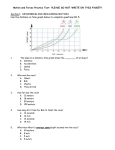
Date: 10/15/2007 Monday Aim: What is the difference between speed & velocity? Do Now: What is motion? Homework: Read pgs 70 – 73 in textbook & Answer Ques. 1 & 2 on pg 72 (Practice Problems) – Write out Formula, Plug in #’s, Calculate & Give Units What is motion? • A change in position over a certain amount of time or, • The movement of an object • The rate at which an object moves (how fast or slow) What is speed? How can speed be calculated? S Speed = Distance Time D T 1) Carl Lewis runs a 100 meter race in 10 seconds. What is his average speed? Avg. Speed = Total distance/Total Time Avg. Speed = 100 m/10 sec Avg. Speed = 10 m/s 2) How much time does it take for a cheetah to travel 84 meters at a speed of 28 m/s? Time = distance/speed T = 84 m 28 m/s T = 3 sec. 3) What distance does a jogger go if she runs with a speed of 160 m/min for 20 minutes? Distance = speed x time D = (160 m/min) (20 min) D = 3,200 m What information does a Distance vs. Time Graph show? *Constant Speed: speed that stays the same Smith’s Trip to Albany Distance (km) Time (hr) 50 100 150 200 1 2 3 4 D 200 I S 150 T 100 A N 50 C E (km) 1 2 3 TIME (hours) 4 What information does a Distance vs. Time Graph show? *Speed Changes Brown’s Trip to Albany Distance (km) Time (hr) 100 100 150 200 1 2 3 4 D 200 I S 150 T 100 A N 50 C E (km) 1 2 3 TIME (hours) 4 What is velocity? A measure of both speed & direction Example: An automobile travels 80 km North in 2 hrs. What is the avg. speed of the car? What is the avg. velocity? V = D V = 80 km Avg. speed = 40 km/hr 2 hr Avg. velocity = 40 km/hr North T Date: 10/28/2007 Friday Aim: 1. What does a distance vs. time graph show? 2. How do velocities add & subtract from each other? Do Now: 1. Take out homework. 2. What is the slope of a distance vs. time graph equal to? Homework: Handout (A Speedy Journey) 20 km (40 km – 20 km) 0.5 h or 30 min 40 km (80 km – 40 km) 1.5 hrs. 5. What is car B’s avg. speed during the first part of this trip? Avg. S = T. Dist. T. Time Avg. S = 40 km 0.5 hr Avg. S = 80 km/hr 6. How fast did cars A & B go together? Avg. S = T. Dist. Avg. S = 40 km Avg. S = 40 km/hr T. Time 1 hr A = VF – VI time A = 0.67 – 0.60 10 A = 0.93 – 0.75 20 12 km / 20 s = 0.60 km/s 20 km / 30 s = 0.67 km/s .007 km/s2 30 km / 40 s = 0.75 km/s 56 km / 60 s = 0.93 km/s .009 km/s2 NO Can velocities add together? Yes, but only if they’re moving in the same direction Example: If you are paddling a boat South at 5 m/s & the stream is moving at 8 m/s South: Are their velocities Your boat will move at: adding together? 13 m/s South Can velocities subtract from each other? Yes, but only if they’re moving in the opposite direction Example: If you are paddling a boat South at 10 m/s & the stream is moving North at 12 m/s: Your boat will move: 2 m/s North What does each picture show? Velocities adding together 6 m/s Right + 10 m/s Right = 16 m/s Right Velocities subtracting 10 m/s Right - 14 m/s Left = 4 m/s Left Date: 10/17/2006 Wednesday Aim: Lab: Measuring the Speeds of People Walking Do Now: 1. Take out homework. 2. Read over lab 3. Answer ques. next slide. Homework: Complete Lab Aim: How can we calculate acceleration? Do Now: 1. Take out Lab & Motion Note-packet 2. Complete Review Questions on pg 6 in your note-packet Homework:Handout #1 #4 #1 None All 4 cars are moving at constant speed Avg. Speed = T. Dist./T. Time __________= 250 km/hr 250 km/1 hr What is acceleration? • The rate at which the velocity of a moving object increases Acceleration =change in velocity What is the time mathematical formula for OR acceleration? a = vfinal – vinitial t 1) What is the acceleration of an ice skater who changes velocity from 5 m/s north to 15 m/s north in 5 seconds? a = 15 m/s – 5 m/s a = vfinal – vinitial 5s t a = 2 m/s2 North 2) How quickly would a race car accelerate if its velocity changed from 0 to 32 m/s in 4 seconds? a = 32 m/s – 0 m/s a = vfinal – vinitial 4s t a = 8 m/s2 What is deceleration? • The rate at which the velocity of a moving object decreases What information does a Velocity vs. Time Graph show? *Constant acceleration Smith’s Trip to Albany Velocity (m/s) Time (s) 7 14 21 28 1 2 3 4 V 28 E L 21 O 14 C I 7 T Y (M/S) 1 2 3 TIME (hours) 4 What is the motion of a freely falling object? Any object falling near the surface of the earth will accelerate at a rate of 9.8 m/s2 due to the pull of gravity. Date: 10/19/2007 Friday Aim: What is Momentum? Do Now: Prepare for Motion Quiz Homework: Study for next week’s Exam on Motion & Forces •Quiz (Motion) • The mass of an object What is momentum? multiplied by its velocity, which determines how difficult it is to stop the object. • The greater the momentum = greater energy the object has What is the mathematical formula for momentum? momentum = mass x velocity or p = mv Date: 10/22/2007 Monday Aim: 1. What is Force? Do Now: 1. What 2 things does momentum depend upon? 2. What are units of momentum? Homework: Study for a Quiz on Forces. What is a Force? A push or a pull that one object exerts on another. What are some examples of a force? Ex) A tow truck pulls a car, The wind pushes a flag, Gravity & Friction What is a Newton? The unit used to measure force Force = Mass X Acceleration 1N = kg m/sec2 . 1. The attractive force between objects 2. Depends on the masses of the objects and the distance between them As mass increases, gravitational pull increases What is gravitational force? As distance increases, gravitational pull decreases Where is the Gravitational Pull the greatest? 1. 50 kg 10 m 2. 10 kg 10 m 10 kg 10 kg Where is the Gravitational Pull the greatest? 1. 2. 10 kg 10 kg 10 m 10 kg 20 m 10 kg What is weight? The weight of an object is equal to the gravitational force exerted by Earth (9.8m/s2) on an object Where will you weigh more: on the Earth or on the Moon? Why? Forces on an object that What are balanced forces? are equal in size & opposite in direction =0 - The net force is zero because the two forces cancel each other out What are unbalanced forces? Unequal forces working against each other produces motion in the direction of the larger force. 10N 4N = 6N *In Opposite Directions, Forces Subtract Date: 10/23/2007 Tuesday Aim: 1. What is Newton’s First Law of Motion? Do Now: Prepare for a Quiz. Homework: Read pgs 98 – 103 & Ans. Ques. (1-4 & 6-7) on pg 103 (self-check) • Quiz (Momentum & Forces) Newton’s Laws of Motion J What is Newton’s 1st Law of Motion? The Law of Inertia 1. Objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. 2. Objects in motion tend to remain in motion (in constant velocity, along a straight path) unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. (such as friction) This is what happens when your not wearing a seatbelt. Since the car is in motion you are also in motion, and when the wall stops the car.You continue to be in motion and fly forward. When the truck is stopped by the car. The ladder continues in motion. What is inertia? The tendency of an object to resist a change in motion. Inertia is related to an objects mass: the more mass an object has the greater its inertia and the more difficult it is to change its motion. Which would have more inertia an empty shopping cart or a full one? Date: 10/24/2007 Wednesday Aim: 1. What are 3 types of friction? Do Now: 1. Take out homework. 2. What is Newton’s First Law of Motion? Homework: Read pgs 104-111 Ans. Ques. (1-4 & 6) on pg 111 (self check) What is friction? 1. Exists wherever 2 surfaces touch. 2. It’s a force that acts in the opposite direction to motion. 3. It causes moving objects to slow down & stop. 4. It always produces heat. What types 1) Sliding Friction – When of friction solid objects slide over each are there? other. 2) Rolling Friction – Friction produced by wheels or ball bearings 3) Fluid Friction – The force exerted by a fluid (Lubricants such as grease & oil) change sliding friction into fluid friction and reduce the overall amount of friction. 1. Lubricants such as oil, What are grease, lotion, water some methods used 2. Wheels (Rolling frictions is less than sliding friction) to reduce 3. Sand on a smooth surface friction? Can friction be good? Yes! In what direction is this object moving? What are 3 forces are acting on this object? Pull Left 2N (Friction) Pull Right 7N How can we decrease the friction? What is friction? Date: 10/25/2007 Thursday Aim: How do force, mass & acceleration relate to each other? Do Now: 1. Take out homework. 2. Describe the 3 types of friction. Homework: Study for tomorrow’s Quiz on Forces What is Newton’s Second Law? Newton’s second law of motion explains how force and acceleration are related What is the Force = Mass X Acceleration equation form of F Newton’s second law? M A Which car will take a greater force to accelerate? How much force is needed to accelerate a 1500kg car at a rate of 3 m/sec/sec? Force = mass x acceleration Force = 1500kg x 3 m/sec/sec Force = 4500N F M A A hockey player shoots a puck with a force of 900 Newtons. The puck has a mass of 1.5kg. At what rate will the puck accelerate? Acceleration = Force Mass Acceleration = 900 N 1.5 kg F M Acceleration = 600 m/s2 A What is the relationship between force & acceleration? As force increases, acceleration increases. Direct Relationship What is the relationship between mass & acceleration? As mass increases, acceleration decreases. Inverse Relationship Date: 10/26/2007 Friday Aim: 1. What is Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion? 2. Quiz on Forces. Do Now: Take out note-packet. Homework: Study for Tuesday’s Motion/Forces Exam What is Newton’s Third Law of Motion? For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Newton's third law. The skaters' forces on each other are equal in magnitude, and in opposite directions • Newton’s Final Quiz STOP • Quiz Section Beyond This Point Quiz (Motion)) 1. Velocity = ________ & ________. 2. A change in position over time is known as _________. 3. If I rollerblade 10 meters in 2 seconds, how fast am I moving? 4. If a car goes 20 km/hr in 0.5 hours how far did it travel? 5. A car went from stop to 30 m/s in 5 seconds. What was the rate of acceleration? GO ON…. These graphs show: 6. 7. GO ON…. 8. Which car is moving the fastest? 9. What pulls everything towards the earth at a rate of 9.8 m/s2? 10.What tools are used to calculate speed? Stop!! Quiz (Momentum &Forces)) 1. Momentum = ________ & ________. 2. A force = a ________ or a _________. 3. Units of force = ______________ 4. As distance increases, gravitational pull ___________. 5. A book is resting (no motion) on the desk & is pushing down with a force of 3N. The desk is pushing up with a force of ________N. STOP!! What is a force? What are balanced forces? What do unbalanced forces cause? What does friction create? A force gives off ? What are units of force? What is a force that opposes motion? STOP!!!