* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 13: Work and Energy - South Kingstown High School
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Rebound effect (conservation) wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
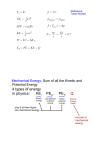
CHAPTER 13: WORK AND ENERGY SECTION 4: CONSERVATION OF ENERGY ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS Energy readily changes from one form to another form. Potential energy can become kinetic energy Kinetic energy can become potential energy Mechanical energy can change to other forms of energy heat, sound Whatever form energy takes during a transformation, the TOTAL AMOUNT of energy ALWAYS REMAINS THE SAME We know where it goes. Can’t always use the new energy form, but it is counted LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Energy cannot be created or destroyed Although energy may change from one form to another, the total amount of energy in the universe never changes Energy does not appear or disappear Also called the First Law of Thermodynamics For any system, the net change in energy equals the energy transferred as work and as heat EFFICIENCY Only a portion of the work done by a machine is useful work Some useful energy is lost due to friction as heat energy. Efficiency measure of how much useful work a machine can do 𝑢𝑠𝑒𝑓𝑢𝑙 𝑤𝑜𝑟𝑘 𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡 𝑒𝑓𝑓𝑖𝑐𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦 = x 100% 𝑤𝑜𝑟𝑘 𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡 EFFICIENCY CONTINUED Efficiency is usually expressed as a percentage. 100% efficient machine means that the machine uses all the work put into it as work done by the machine This is impossible in the real world, because of friction This means that perpetual motion machines are impossible. Machines need energy input