* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Virtual work wikipedia , lookup
Rubber elasticity wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Mohr's circle wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Machine (mechanical) wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Definition of “Mechanics”
Science concerned with the motion of bodies under
the action of forces, including the special case in
which a body remains at rest. Of first concern in the
problem of motion are the forces that bodies exert
on one another. This leads to the study of such topics
as gravitation, electricity, and magnetism, according
to the nature of the forces involved. Given the forces,
one can seek the manner in which bodies move
under the action of forces; this is the subject matter
of mechanics proper.
-------Encyclopædia Britannica
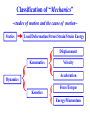
Classification of “Mechanics”
~studies of motion and the cause of motion~
Statics
Load/Deformation/Stress/Strain/Strain Energy
Kenematics
Dynamics
{
Kenetics
{
Displacement
{
Force/Torque
Velocity
Acceleration
Energy/Momentum
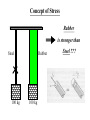
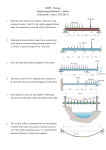
Concept of Stress
Rubber
is stronger than
Steel
100 kg
Rubber
100 kg
Steel ???
From Force to Stress
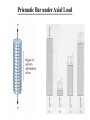
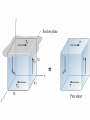
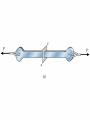
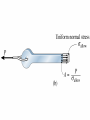
Prismatic Bar under Axial Load
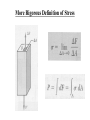
More Rigorous Definition of Stress
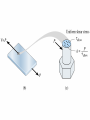
Shear Force and Shear Stress
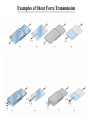
Examples of Shear Force Transmission
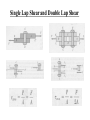
Single Lap Shear and Double Lap Shear
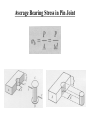
Average Bearing Stress in Pin Joint
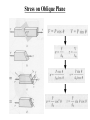
Stress on Oblique Plane
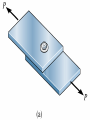
Stress under General Loading
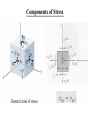
Components of Stress
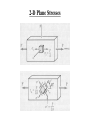
2-D Plane Stresses
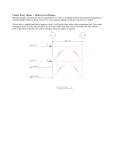
Allowable Stress and Safety Factor
su
sa?
sallowable = sultimate /(Safety Factor)