* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Frictional contact mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
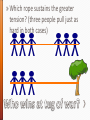
» A box weighing 100 N is pushed on a horizontal floor. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.2. » What acceleration will result if a person applies a horizontal force of 40 N? » Don’t even begin to calculate anything until you have drawn a FBD!!!!!!! a) Horizontally: Fnet = Fapplied - Ffriction Fnet = 40 - (0.2) (100) = 20 N Now, we want to find the acceleration using F = ma F =ma 20 = 10.2 a where m= W/g a = 1.96 m/s2 » Forces are often applied by means of cables or ropes that are used to pull an object. » A force, T, is applied to the right end of a rope attached to a box. » Each particle in the rope in turn applies a force to its neighbor. » As a result the force is applied to the box. » How does the tension in the left end of the rope compare with the tension in the right end? » Which rope sustains the greater tension? (three people pull just as hard in both cases) » When we look at problems with tension, we assume that we are using a “mass-less” rope. » No net force is needed to accelerate a “mass-less” rope, so we can ignore it (otherwise you need to use calculus!) » An elevator has a mass of 1000kg. It accelerates upward at 3m/s2. What is the force, FT, exerted by the cable on the elevator? FT (tension from the cable) ∑F = FT - FW = ma F T – 1000(9.8) = 1000(3) FT = 12,800 N FW (weight of elevator) » An elevator has a mass of 1000kg. The elevator is at rest. What is the force, FT, exerted by the cable on the elevator? FT (tension from the cable) ∑F = FT - FW = ma F T – 1000(9.8) = 0 FT = 9,800 N FW (weight of elevator) » The ability of a mass-less rope to transmit tension undiminished from one end to the other is NOT affected when the rope passes around a pulley » The ability of a mass-less rope to transmit tension undiminished from one end to the other is NOT affected when the rope passes around a simple pulley (one end is stationary) » A window washer on a scaffold is hoisting the scaffold up the side of a building by pulling downward on a rope. The pulling force is 540N and the mass of the worker and scaffold is 155kg. What is the acceleration of the unit? » An object is in equilibrium when it has zero acceleration. » Zero acceleration means constant velocity. (0 m/s is also constant velocity) » Equilibrium means that the forces are balanced in each direction (x, and y) » ΣFx = 0 » ΣFy = 0 » Make sure to resolve all vectors into xand y-components. » ΣFx = 0 » ΣFy = 0 » An object is NOT in equilibrium if it is accelerating, meaning there is an unbalanced force(s) » Make sure to resolve all vectors into xand y-components. » ΣFx = max » ΣFy = may » Use a triangle to find the resultant acceleration