* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sparta & Athens - RoshanVarghese
Athenian democracy wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of Greece and the Greek world wikipedia , lookup
Greek mythology wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Peloponnesian War wikipedia , lookup
Spartan army wikipedia , lookup
Corinthian War wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Persian Wars wikipedia , lookup
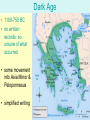
WarmUp #1 • Read the box on pg. 131 on mythology & answer the respective question. • Read pg. 149 on Greek drama & answer the respective questions. ANCIENT GREECE: SPARTA & ATHENS The Geography of Greece: mountainous terrain & islands kept city-states isolated from each other Early Peoples of Greece Minoans • 2700-1450 BC on the island of Crete • peaceful traders • king’s palace had many rooms – bright paintings of rural/sporting scenes • scholars/historians are unable to decipher their writing • destroyed by Mycenaean invasion in 1450 BC • • • • • • Mycenae 1600-1100 BC on the mainland of Greece loose alliance of independent city-states warriors: decorations in homes showed battle/hunting scenes traders extended land through conquest (Minoans) most famous story from Homer = The Iliad (Trojan War) fell into trouble as numerous conflicts between city-states, earthquakes, invasions, etc. Minoan Civilization Trojan War (~1250 BC) • king of Mycenae (Agamemnon) led Greek troops in the sacking Troy, as revenge • speculation that war was either over Helen (of Troy) OR over trade routes • historians debate the reality of Trojan War Homer • most famous Greek poet – composed epic poems: literature involving heroic event(s) &/or person(s) • most famous poems are: – The Iliad: the last year of Trojan War with the climactic battle between Hector & Achilles – The Odyssey: The travels of Odysseus on his way home post-Trojan War • Homer’s poems used to teach history, literature, honor & courage Dark Age • 1100-750 BC • no written records: so unsure of what occurred • some movement into Asia Minor & Peloponnesus • simplified writing City-States • polis: Greek city-states • acropolis: fortified area within polis (the main gathering place) • agora: open area under the acropolis (the market) • people were extremely loyal to their own polis & thus distrusted all others • army made up of hoplites: heavily armed infantry (i.e. foot soldiers) – phalanx: fighting formation, in which soldiers stood shoulder to shoulder, in a rectangular formation Government • Greeks wanted rule of law: all citizens must obey the laws (including king(s), priests, merchants, etc.) description example Monarchy rule by one Sumer, Akkad, etc. Theocracy rule by God Israel Democracy rule of many Direct Democracy all citizens vote on every issue Athens Oligarchy rule by the few Sparta Republic rule by elected officials Rome Sparta • incredibly militaristic Sparta – men in the army & women supported the army • men: – lived, ate & practiced together in barracks – very disciplined: no frills & simple food (black broth) • boys: – military training began at age 7 • women: – took care of home – physically fit with large families – taught honor (shield story) • government: – oligarchy w/ 2 kings & council of elders • people were intellectually isolated from world – no travel – no philosophy or art taught – no questioning of Spartan ways Sparta (ctnd) – “This Is Sparta” from 300: • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QkWS9PiXekE – “Spartan Phalanx” from 300: • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XR1l01cZQV0 Athens Athens • the governmental structure continued to evolve: – monarchy>aristocratic oligarchy>direct democracy • direct democracy: every male citizen to have a say & then vote on every issue • 3 types of people: – citizens WITH rights (men) – citizens WITHOUT rights (women & children) – non-citizens (slaves & foreigners) • emphasized art, philosophy & culture Greek Religion • considered religion necessary for welfare of state • tried to know will of gods through oracles: – priests/priestesses in temples, that were setup for the gods – most famous oracle: Delphi (purposefully vague) • polytheistic: 12 main gods/goddesses – Zeus: chief god – Athena: goddess of wisdom – Apollo: god of sun -Poseidon: god of seas -Aphrodite: goddess of love -Ares: god of war • tried to gain favor of gods through competitions/festivals (Olympics, etc.) • after death, people went to dim place ruled by Hades Greek Religion Persian Wars (~492-449 BC) • Persians ruled Ionia • 499 BC: Athens helped Ionians revolt • Persians landed at Marathon (26.2 miles from Athens) for battle • Athenians scored shocking/decisive victory; Pheidippes ran to Athens to declare victory, dying at journey’s end • Xerxes marched troops over to Greek mainland • Greeks were far outnumbered • Spartans held pass at Thermopylae, allowing other Greeks to regroup • Persians were defeated by Athenian navy at the Battle of Salamis & finally forced out by the Spartan army at the Battle of Plataea. THE GREEKS WON! Persian Wars Classwork→Homework • Chp. 5: Section 1, 2, & 3 Assessments – Section 1: #1-3 – Section 2: #1-4 – Section 3: #1-3