* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 12-3 Cardiac Cycle
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
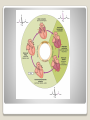
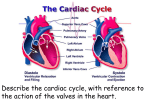
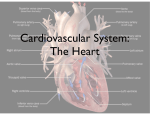
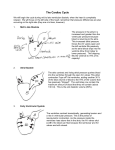
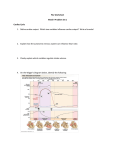
12-3 Cardiac Cycle Jocelyn Sassano & Sarah Miller The period between the start of one heartbeat and the start of the nest is a single cardiac cycle Can be divided into two phases: ◦ During contraction, or systole, the chamber squeezes blood into adjacent chamber ◦ Relaxation, or diastole, follows where the chamber fills with blood and prepares for the start of the next cardiac cycle ◦ Fluids move from an area of higher pressure to lower pressure. An increase in pressure in one chamber causes blood to flow into another chamber. The Cardiac Cycle 1. ◦ ◦ 2. ◦ ◦ Atrial Systole: The atria are filled with blood, and the ventricles are partially filled with blood, and the ventricles are partially filled with blood The atria contract, completely filling the ventricles with blood Atrial Diastole and Ventricular Systole: The AV valves swing shut as pressure in the ventricles rise Blood pushes open the semilunar valves and flows into the aorta and pulmonary trunk Phases of the Cardiac Cycle 3. Ejection phase of Ventricular systole ◦ Pressure in the ventricles rises higher than arties ◦ Blood pushes open the semilunar valves and flows into the aorta and pulmonary trunk 4. Ventricular Diastole ◦ Semilunar valves close as ventricular pressures decline ◦ As ventricular pressures fall below atrial pressures, the AV valves open and blood flows from the atria into the ventricles Phases of the Cardiac Cycle Stethoscopes are used to listen for four heart sounds ◦ The first heart sound (“lubb”) is produced as the AV valves close and semilunar valves open ◦ The second heart sound (“dupp”) occurs at the beginning of the ventricular diastole when the semilunar valves close ◦ Third and Fourth heart sounds may be audible as well, but they are very faint and rarely detectable Associated with atrial contraction and blood flowing into the ventricles Heart Sounds