* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transition Metals & Complex ions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
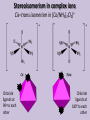
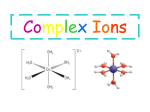
Transition Metals & Complex ions • State and give examples of complexes with six-fold coordination with an octahedral shape • Describe and use the terms: complex ion and coordination number. • Explain the term ligand in terms of coordinate bonding. Definition Hangman – Coordinate bond (aka – dative covalent bond) _A/ shared _ _ _ _ _ pair _ / _ _of_ electrons _ / _ _ / _ _ in _ _which _____ /the _ _ /bonded _ _ _ _ _ pair / _ _ _has / _ been _ _ _ _ provided _/____/ ___/____/________/__/___/ by one of the bonding atoms only. _ _ / _ _ _ / _ _ _ _ _ _ _ / _ _ _ _ _ / _ _ _ _. Complex ion [Fe(H2O)6]2+ Each of the six H2O ligands forms one coordinate (dative covalent) bond to the central metal ion using a lone pair of electrons from its oxygen atom. This complex ion has a coordination number of six (the number of coordinate bonds to the central metal ion) Charges on complex ions The overall charge of a complex ion is the sum of the individual charges of the transition metal ion and those of the ligands. Name of ligand Formula Charge Water :OH2 None - neutral Ammonia Thiocyanate :NH3 :SCN- None - neutral -1 Cyanide :CN- -1 Chloride Hydroxide :Cl:OH- -1 -1 Example State the formula and charge of the complex ion made from one Iron (II) ion and 6 cyanide molecules. [Fe(CN)6]4- All of these ligands are classed as monodentate ligands (i.e. They only donate one pair of electrons to the central metal ion) Formulae Questions 1. State the formula & charge of each of these complex ions: a) One copper (II) ion & four chloride ions b) One iron (III) ion & five water molecules & a chloride ion. c) One copper (II) ion & four ammonia molecules & two hydroxide ions d) One cobalt (III) ion & four hydroxide ions 2. What is the oxidation number of the transition metal in each of these complex ions. a) b) c) d) [Fe(CN)6]3[Co(SCN)4]2[Cu(CN)4(Cl)2]4[Ti(H2O)3OH]2+ 3D shapes of complex ions Most common shape = octahedral ( 6 coordinate bonds) BOND ANGLE = all 90o 3D shapes of complex ions Less common shape = tetrahedral ( 4 coordinate bonds) BOND ANGLE = all 109.5o The copper(II) and cobalt(II) ions have four chloride ions bonded to them rather than six, because the chloride ions are too big to fit any more around the central metal ion. Shapes of complex ions Questions For each of the 8 complex ions you worked with during “formulae questions” draw the 3D shape using the wedge shaped bonds, show the bond angles and name the shape. Reminder – what is a stereoisomer? • Molecules or complexes with the same structural formula but with a different arrangement of the atoms in space. Stereoisomerism in complex ions Cis–trans isomerism in [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+ Chloride ligands at 90o to each other Chloride ligands at 180o to each other Stereoisomerism in complex ions Cis–trans isomerism in [NiCl2(NH3)2] 4 coordinate bonds – alternative to tetrahedral = Square Planar BOND ANGLE = all 90o Structure of cis-platin Effective cancer treatment – Thought to bind to and alter cancer cell DNA and therefore prevent their growth and reproduction 1. What is the formula for cis-platin? 2. Explain why this molecule uses the prefix “cis” in its name.