* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Cycle 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
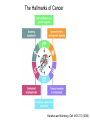
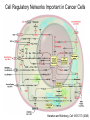
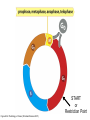
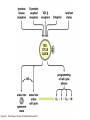
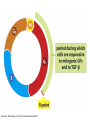
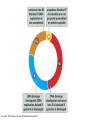
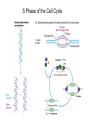
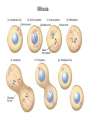
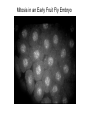
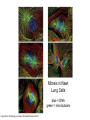
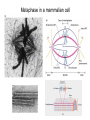
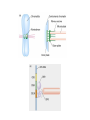
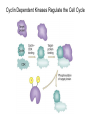
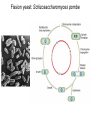
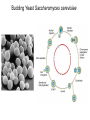
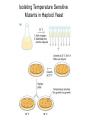
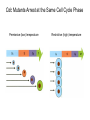
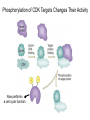
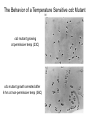
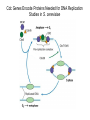
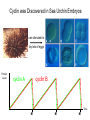
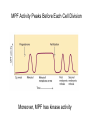
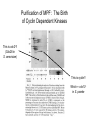
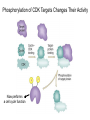
The Hallmarks of Cancer Hanahan and Weinberg, Cell 100:57-70 (2000) Cell Regulatory Networks Important in Cancer Cells Hanahan and Weinberg, Cell 100:57-70 (2000) START or Restriction Point Figure 8.3b The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007) Figure 8.1 The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007) Figure 8.6 The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007) The Main Jobs of the Cell Cycle: 1. To accurately transmit the genetic information! 2. To maintain normal ploidy; i.e. diploidy! Euploidy: additions of whole chromosome sets e.g. n, 2n, 3n, 4n = haploid, diploid, triploid, tetraploid Aneuploidy: additions or subtractions of one or more single chromosomes e.g. 2n + 1, 2n -1, 2n + 2, etc. Figure 8.4 The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007) Properties Required for Transmission of Chromosomes During Cell Division 1. One and only one centromere 2. Functional telomere at both ends 3. Chromosomes must be fully replicated 4. Chromosomes cannot be too large or too small S Phase of the Cell Cycle Mitosis Mitosis in an Early Fruit Fly Embryo Mitosis in Newt Lung Cells blue = DNA green = microtubules Figure 8.3a The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007) Metaphase in a mammalian cell Anaphase in a plant cell G1-S and G2-M are the major control points in the cell cycle 1. Fuse M phase cell with interphase cell: Interphase nucleus enters M 2. Fuse S phase cell with G1 cell: The G1 nucleus enters S phase 3. Fuse S phase cell with G2 cell: The G2 nucleus does not enter S phase Rao and Johnson cell fusion experiments Cyclin Dependent Kinases Regulate the Cell Cycle Experimental Systems Important for Cell Cycle Studies Saccharomyces cerevisiae Schizosaccharomyces pombe Arbacia punctulata Xenopus laevis Fission yeast: Schizosaccharomyces pombe Budding Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae Isolating Temperature Sensitive Mutants in Haploid Yeast Cdc Mutants Arrest at the Same Cell Cycle Phase Permissive (low) temperature Restrictive (high) temperature Phosphorylation of CDK Targets Changes Their Activity Now performs a cell cycle function The Behavior of a Temperature Sensitive cdc Mutant cdc mutant growing at permissive temp (23C) cdc mutant growth arrested after 6 hrs at non-permissive temp (36C) How to Clone cdc Genes in Yeast Cdc Genes Encode Proteins Needed for DNA Replication Studies in S. cerevisiae Cdc Genes Encode Proteins Needed for the G2-M Transition: Studies in S. pombe cdc2+ encodes a kinase Moreover = cdc28 in S. cerevisiae! Cyclin was Discovered in Sea Urchin Embryos can stimulate to lay lots of eggs Protein Level cyclin A cyclin B Time M M M mitosis mitosis mitosis (Spisula is actually a clam.) Overview of the frog life cycle OOCYTE GROWS WITHOUT DIVIDING (MONTHS) FERTILIZATION FERTILIZED EGG DIVIDES WITHOUT GROWING (HOURS) 1 mm sperm tadpole feeds, grows and becomes an adult frog The Maturation of Frog Eggs The Maturation of Frog Eggs An Assay for Maturation Promoting Factor (MPF) Yoshio Masui, 1971 MPF Activity Peaks Before Each Cell Division Moreover, MPF has kinase activity Purification of MPF: The Birth of Cyclin Dependent Kinases This is cdc2+!! (Cdc28 in S. cerevisiae) This is cyclin!! Which = cdc13+ in S. pombe Phosphorylation of CDK Targets Changes Their Activity Now performs a cell cycle function The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, 2001 “for their discovery of key regulators of the cell cycle”