* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (c) enzyme
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
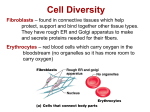
Dr.Srirath Pakdeeronachit List the simplest to the most complex levels of a living organism. Describe the main parts of a cell. Label a diagram of a typical cell. Name and give the functions of the four basic types of tissues in the body. Define basic terms pertaining to the structure and function of body tissues. Recognize and use roots and suffixes pertaining to cells, tissues, and organs. 1. The root that means “cell” is: (a) spher (b) cyt (c) fibr (d) gen 2. The root that means “tissue” is: (a) hist (b) cellul (c) cyst (d) hem 3. The control center of the cell is the: (a) membrane (b) ribosome (c) virus (d) nucleus 4. The process of body cell division is called: (a) separation (b) segregation (c) mitosis (d) gestation 5. A compound that speeds the rate of a metabolic reaction is a(n): (a) gene (b) salt (c) enzyme (d) mineral 6. The substance that makes up the cell’s genetic material is: (a) DNA (b) protein (c) acid (d) base 7. Chemicals: cells: tissues: __________: systems: organism. What belongs in the blank? (a) organs (b) genes (c) enzymes (d) nuclei 8. The root morph/o means: (a) reproduction (b) fat (c) form (d) balance Simple Complex Basic unit of living organisms Carries out metabolism Energy generated by chemical ATP (adenosine triphosphate) Nucleus - the control region of the cell - contains chromosome (genetic information) - DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) Gene - RNA (Ribonucleic acid) Root Meaning Example Definition of Example morph/o form polymorphous having many forms cyt/o, -cyte cell cytologist one who studies cells nucle/o nucleus nuclear pertaining to a nucleus kary/o nucleus karyotype picture of a cell's chromosomes organized according to size hist/o, histi/o tissue histocompatibility tissue similarity that permits transplantation fibr/o fiber fibrosis abnormal formation of fibrous tissue reticul/o network reticulum a network Root Meaning Example Definition of Example aden/o gland adenoma tumor (-oma) of a gland papill/o nipple papilla projection that resembles a nipple myx/o mucus myxadenitis inflammation (-itis) of a mucussecreting gland muc/o mucus, mucous membrane mucorrhea increased flow (-rhea) of mucus somat/o, -some body, small body chromosome small body that takes up color (dye) (chrom/o) Stages in Cell Division “Mitosis” Dividing of body cell Root Meaning Example Definition of Example blast/o, blast immature cell, productive cell, embryonic cell histioblast a tissue-forming cell gen origin, formation karyogenesis formation of a nucleus phag/o eat, ingest autophagy self-destruction of a cell's organelles phil attract, absorb basophilic attracting basic stain plas formation, molding, hyperplasia development overdevelopment of an organ or tissue trop act on, affect chronotropic affecting rate or timing (chron/o) troph/o feeding, growth, nourishment atrophy tissue wasting Cell Fiber Histology Form Nucleus Nucleus Gland Nipple Mucous Network Mucous Body Morphology Cytology Histology d c e b a d c e b a gen phag/o blast/o plas troph/o origin, formation eat, ingest immature, productive, embryonic cell formation, molding, development feeding, growth, nourishment Chromosomes Carry genetic information 46 chromosomes in every cell (except sex cells) Genes Separate units of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) Control formation of enzymes (needed for metabolic reactions) Four basic types Epithelial Covers and protects body structures, lines organs, vessels, and cavities Simple: Single layer, absorbs substances from one system to another Stratified: multiple layers, protects deeper tissue Four basic types Connective Supports and binds body structures Muscle (root: my/o) Contracts to produce movement Three types: skeletal, cardiac, smooth/visceral Nervous (root: neur/o) Makes up brain, spinal cord and nerves Coordinates body responses by transmission of electrical impulses Simplest tissue Mucous membranes: secrete mucus Serous membranes: secrete watery fluid, line body cavities and cover organs Fibrous membranes: cover and support organs Organs Comprised of tissues Grouped into systems Systems Have specific function Work together, not independently Goal of systems: homeostasis Organs of Digestive Tract Proteins Enzymes Hormones Structural materials Carbohydrates Sugars (main energy source: sugar glucose) Starches Lipids Fats Word Part Meaning Example Definition Of Example -ase enzyme lipase enzyme that digests fat (lipid) -ose sugar lactose milk sugar hydr/o water, fluid hydration addition of water; relative amount of water present gluc/o glucose glucogenesis production of glucose glyc/o sugar, glucose normoglycemia normal blood sugar level Suffixes Roots Word Part Meaning Example Definition Of Example sacchar/o sugar polysaccharide compound containing many simple sugars amyl/o starch amyloid resembling starch lip/o lipid, fat lipophilic attracting or absorbing lipid adip/o fat adiposuria presence of fat in the urine (ur/o) steat/o fatty steatorrhea discharge (-rhea) of fatty stools prote/o protein protease enzyme that digests protein Roots sugar sugar water, fluid starch lipid, fat glucose fat steat/o lip/o glyc/o gluc/o fat fat sugar glucose 1. The root that means “cell” is: (a) spher (b) cyt (c) fibr (d) gen 2. The root that means “tissue” is: (a) hist (b) cellul (c) cyst (d) hem 3. The control center of the cell is the: (a) membrane (b) ribosome (c) virus (d) nucleus 4. The process of body cell division is called: (a) separation (b) segregation (c) mitosis (d) gestation 5. A compound that speeds the rate of a metabolic reaction is a(n): (a) gene (b) salt (c) enzyme (d) mineral 6. The substance that makes up the cell’s genetic material is: (a) DNA (b) protein (c) acid (d) base 7. Chemicals: cells: tissues: __________: systems: organism. What belongs in the blank? (a) organs (b) genes (c) enzymes (d) nuclei 8. The root morph/o means: (a) reproduction (b) fat (c) form (d) balance 1. The root that means “cell” is: (a) spher (b) cyt (c) fibr (d) gen 2. The root that means “tissue” is: (a) hist (b) cellul (c) cyst (d) hem 3. The control center of the cell is the: (a) membrane (b) ribosome (c) virus (d) nucleus 4. The process of body cell division is called: (a) separation (b) segregation (c) mitosis (d) gestation 5. A compound that speeds the rate of a metabolic reaction is a(n): (a) gene (b) salt (c) enzyme (d) mineral 6. The substance that makes up the cell’s genetic material is: (a) DNA (b) protein (c) acid (d) base 7. Chemicals: cells: tissues: __________: systems: organism. What belongs in the blank? (a) organs (b) genes (c) enzymes (d) nuclei 8. The root morph/o means: (a) reproduction (b) fat (c) form (d) balance