* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TAKS Review - SchoolNotes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
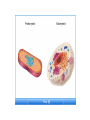
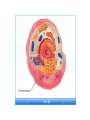
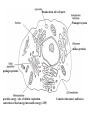
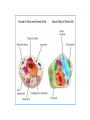
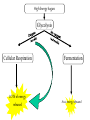
TAKS Review Cell Structure, Function And Energy Breaks down old cell parts Transport system makes proteins packages proteins provides energy : site of cellular respiration, conversion of food energy into usable energy (ATP) Controls what enters and leaves Cell Part Function Cell membrane Nuclear membrane Controls what enters and leaves the cell Controls what enters and leaves the nucleus Nucleus Chromosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Control center of the cell Genetic information in the nucleus Transport system in cell Ribosome Golgi Body Vacuole Lysosome Organelle makes proteins Organelle packages proteins Stores water and/or waste Breaks down old cell parts Mitochondria Organelle for cellular respiration – provides energy Practice Question Which of these is a characteristic of body cells that require large amounts of energy? A They have a large number of mitochondria. B They have a supplementary Y chromosome. C They have a two-layer membrane.A D They have a storage area for albumin Cellular Energy Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Converts sunlight energy into high energy sugars Converts high energy sugars into usable energy (in the form of ATP) Takes place in the chloroplast Takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria Occurs mainly in plants and some bacteria Occurs in all organisms Photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy 6O2 + C6H12O6 carbon dioxide + water + sunlight oxygen + glucose Cellular Respiration 6O2 oxygen + C6H12O6 6CO2 + glucose + 6H2O + Energy carbon dioxide + water + ATP High Energy Sugars Glycolysis Cellular Respiration LOTS of energy released Fermentation A little energy released Practice Question Energy conversion within an animal cell would be severely limited by removal of the cell’s — A mitochondria B chloroplasts C plastids D lysosomes A Practice Question Which molecule provides most of the energy used to drive chemical reactions in cells? F DNA G RNA H ATP J ADP H Transport across the membrane Purpose: to move nutrients and wastes in and out of the cell and maintain…Homeostasis The lipid bilayer is selectively permeable; only small, nonpolar molecules can pass. Other molecules need carrier or channel proteins. •Concentration is a measurement of the amount of solute (in grams) compared to the volume of the solution (in liters) •Grams per liter or g/L •Concentrations change as particles and/or water move into or out of the cell Movement can be passive or active. PASSIVE ACTIVE NO energy required Needs energy Simple diffusion Facilitated diffusion Osmosis Endocytosis Pinocytosis Phagocytosis Exocytosis Diffusion vs. Osmosis • Diffusion is the movement of PARTICLES from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration • Osmosis is the movement of WATER from areas of low solute concentration to areas of high solute concentration; water moves because the particles can’t Salt is a solute. When it is concentrated inside or outside the cell, it will draw the water in its direction. This is why you get thirsty after eating something salty. Simple Rule to remember: SALT SUCKS What is Active Transport? Energy is used to move selected molecules into a cell, even if they are at a low concentration. Practice Question Saltwater fish remove extra salt from their body by active transport through the gills. What is the result of this activity? B A The salt becomes more chemically active. B Water balance is maintained in the blood. C The rate of energy production is decreased. D The cell membrane becomes less permeable to water. Practice Question When a sea urchin egg is removed from the ocean and placed in freshwater, the egg swells and bursts. Which of these causes water to enter the egg? A Coagulation B Sodium pump C Active transport D Osmosis D Practice Question On a hot summer day, a road-crew worker perspires and then feels thirsty as her body temperature increases. This response is an example ofA. releasing enzymes B. decreasing respiration C. assimilating proteins D. maintaining homeostasis D Practice Question Which of these is a function of the cell membrane in all cells? A Producing cellular nutrients B Preserving cellular wastes C Neutralizing chemicals D D Maintaining homeostasis