* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AH exit Exam Review PPT
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
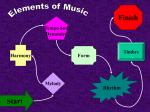
Arts and Humanities Exit Exam MUSIC REVIEW Elements of Music • • • • • • • Rhythm Tempo Melody Harmony Form Timbre Dynamics Rhythm • The pattern of notes and rests • Important Rhythm Terms – Syncopation • Placing emphasis on the weak or off beats – Meter • (AKA Time Signature) • 3 Types – Simple: 4/4 – Compound: 6/8 – Asymmetrical: 5/4 Note and Rest Values • Whole Note= 4 beats • Half Note= 2 beats • Quarter Note= 1 beat • Eighth Note= ½ beat • Sixteenth Note= ¼ beat Tempo • The speed of the music • Accelerando – Gradually speed up • Ritardando – Gradually slow down Tempo Markings • Largo – Very slow • Andante – Walking speed • Moderato – Medium speed • Allegro – Fast tempo • Presto – Very fast Melody • The main part of the song that can be hummed by the listener • Key Signature – Sharps and flats placed @ the beginning of the music that show the scale on which the music is based. Harmony • Two or more notes sounded together • Consonance – Harmony that is pleasing to the listener • Dissonance – Harmony that is “harsh” to the listener Form • The way the music is organized • Opera Forms – Overture • Introduction for operas and ballets – Aria • Song for solo voice that is very melodic in character – Recitative • Song sung in a speaking manner Types of Forms • AB – 2 contrasting sections • ABA – 2 contrasting sections that repeats back to the 1st section • Call and Response – One group performs and another group echoes • Theme and Variations – Basic melody performed in a variety of ways Timbre • The unique characteristic of sound • VOCAL TIMBRES – Soprano • High Female Voice – Alto • Low Female Voice – Tenor • High Male Voice – Bass • Low Male Voice INSTRUMENT FAMILIES • Woodwind – Flute, Clarinet, Saxophone, Oboe, Bassoon • Brass – Trumpet, French Horn, Trombone, Tuba • String – Violin, Viola, Cello, Double Bass, Guitar • Percussion – Drums, Xylophone, Tambourine, Cymbals Dynamics • The loudness or softness of music • • • • • • Pianissimo (pp) Piano (p) Mezzo Piano (mp) Mezzo Forte (mf) Forte (f) Fortissimo (ff) Very Soft Soft Moderately Soft Moderately Loud Loud Very Loud Music Symbols • Staff • Treble Clef • Bass Clef • Sharp • Flat • Natural Symbols, cont. • Crescendo • Decrescendo • Accent • Fermata • Coda More symbols • DC- Repeat to the beginning • DS- Repeat to the sign • Fine-The End Renaissance Period • Most important composer – Giovanni Palestrina • He utilized the “counterpoint” system Baroque Period • Important Composers – George Frederic Handel • Known for oratorios (“The Messiah”) – Johann Sebastian Bach • Cantatas for his church services • Fugue- An imitative style of composition developed during this period Classical Period • Important Composers – Franz Josef Haydn • “The father of the Symphony” – Ludwig Van Beethoven • Most well known is his “5th Symphony” Romantic Period • Important Composers – Richard Wagner • Known for his operas • Ride of the Valkyries • The Flying Dutchman – Peter Tchaikovsky • Known for his ballets • The Nutcracker, Swan Lake, Romeo & Juliet Impressionism • Important Composers – Claude Debussy – Maurice Ravel • Both composers incorporated symbolism into their music Modern Period • Jazz Music – Combines spirituals, blues, and improvisation to create a new and unique style • Improvisation – To create music spontaneously (“on the spot”) American Music • George Gershwin – Incorporated Jazz elements into classical music – Rhapsody in Blue – An American in Paris • Aaron Copland – Used American folk songs and ideas in his music – Appalachian Spring – Billy the Kid • Duke Ellington – Helped shape jazz styles in American music – Take the A Train – Mood Indigo Purposes of Music • Ceremonial – Music for ceremonies and rituals – Star Spangled Banner, Wedding March • Artistic – Music used to express emotion – Ballet Music • Recreational – Music for Fun – Dance Music The End (FINE)