* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Astronomical Unit (AU)
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Fermi paradox wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Big Bang nucleosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Hubble's law wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic microwave background wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Ultimate fate of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Flatness problem wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
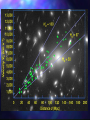
Big Bang Theory Investigative Science What is a Theory? • Well-established idea that is supported by scientific evidence. • Theory statements can be refuted, but not verified, no matter how strongly we believe in the truth of a theory. It is always possible for it to be falsified. How do we measure distances in space? • Astronomical Unit (AU) – average distance between the Earth and the Sun • About 93 million miles • Light-year – the distance that light travels in a year • Used to measure distance to stars and galaxies • Nearest stars are several light-years away What is the size scale in space? • Put the following in order from smallest to largest: • • • • • • • Galaxy Universe Planet Star Comet Solar system Asteroid What is the size scale in space? • Put the following in order from smallest to largest: • • • • • • • Comet Asteroid Planet Star Solar system Galaxy Universe What is Hubble’s Law? • Hubble then noticed a correlation between the distance of the galaxies and the speed at which they are moving away from us • The farther away the galaxy, the faster it is receding (moving away) from the Earth. So if the universe is expanding, then it must have had a beginning. What is the Big Bang Theory? • Universe formed 12 to 14 billion years ago • At “time zero” universe was an explosion of a primeval atom. • Temperatures extremely high at beginning • Expanded rapidly, temperatures dropped • Matter formed from original energy What evidence is there for the Big Bang Theory? • Cosmic background radiation: radiation left over from the initial moments of Big Bang spread evenly around the universe. • Red Shifted galaxies indicating that they are moving away from our galaxy. • Galaxies and stars formed from cooling energy. • Leftover heat from the original explosion • Big Bang model describes our current understanding of the universe. • New discoveries, such as dark matter and accelerating expansion (Dark Energy), lead us to refine our model, but there is no crisis in our understanding (yet). • Science is an ongoing process - forcing us to test our model through prediction and observation. The more tests it passes, the greater is our confidence in it.