* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SNC 1D The Sun
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
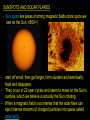
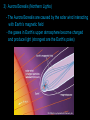
The Sun FORMATION OF THE SOLAR SYSTEM Solar Nebula Theory - states that stars and planets form together from contacting, spinning disks of gas and dust. Nebula - a cloud of gas and dust How did our solar system form? a) a supernova (big explosion where the entire outer part of a star is blown off) sends waves in space that triggered a nebula to start spinning b) as the nebula spins, it begins to collapse as gravity pulls the gas and dust together http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tFLOsRSuW0E&feature=related c) the cloud spins faster and flattens the dust and gas into a disc d) the gas and dust collect in the centre forming a hot condensed lump of matter (protostar) which eventually becomes a star e) small amounts of matter in the disc collect and form bigger, rocky lumps called planetismals. f) those planetismals that survive collisions turn into planets OUR STAR – THE SUN - as the nebula contracts, the gases that collect in the centre compress increasing the temperature of the protostar - when temperatures reach 10 000 000oC we get: NUCLEAR FUSION! Nuclear Fusion -the process that produces energy in the Sun. -Hydrogen nuclei combine to form helium nuclei. -Takes a lot of pressure and temperature -Nuclear reaction http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fSr3V498A3I&feature=related PARTS OF THE SUN CORE - gravity pulls all the mass inwards creating intense pressure forcing hydrogen atoms to come together (nuclear fusion) to make helium atoms - Energy is transferred from core to outer parts by RADIATION. - The outer layers transfer energy by CONVECTION CURRENTS. Structure of the Sun PHOTOSPHERE - called the surface of the Sun (not really a surface since the Sun is made up of gases) - 5500oC; thousands of km deep CHROMOSPHERE - the inner atmosphere Structure of the Sun CORONA - the hot outer part of the Sun (1 000 000 oC) A GROWING SUN - Helium is denser than hydrogen and settles in the Sun’s core - Helium core grows larger as well as the fusion area around it - Sun is getting larger; 30% larger than when it was born 5 billion years ago - Sun has enough hydrogen fuel (for fusion) for 10 billion years Our Sun has 5 billion more years left SUNSPOTS AND SOLAR FLARES - Sun spots are areas of strong magnetic fields (dark spots we see on the Sun; 4500oC) - - start off small, then get larger, form clusters and eventually fade and disappear. They occur in 22-year cycles and seem to move on the Sun’s surface, which we believe is actually the Sun rotating. When a magnetic field is so intense that the solar flare can eject intense streams of charged particles into space called solar wind. SOLAR WIND – How does it affect Earth? 1) Disrupt telecommunications and damage equipment aboard spacecrafts 2) Harmful to astronauts (like x-rays on humans) 3) Aurora Borealis (Northern Lights) - The Aurora Borealis are caused by the solar wind interacting with Earth’s magnetic field - the gases in Earth’s upper atmosphere become charged and produce light (strongest are the Earth’s poles) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xUYibQFIIVk&feature=PlayList&p=60FA28 55CF33865F&index=45 IMPORTANCE OF THE SUN 1. Provides radiant energy for all life on Earth 2. Keeps Earth in a steady orbit because of its gravitational pull. 3. Creates winds and ocean currents 4. Microwaves, radio waves, X-rays, gamma rays http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gdLaPhNBOcU&feature=related