* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nebula - NICADD
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Orion (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Crab Nebula wikipedia , lookup
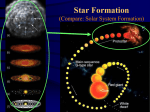
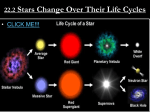
Nebula Fuzzy Patch • Any source of light in the night sky that was not a point was called a nebula. – – – – – comets gas clouds dust clouds galaxies star clusters • In order to help comet hunters, Charles Messier began to catalog these objects in the 1700’s. Interstellar Medium • Interstellar space is 99% gas. – Hydrogen 74% – Helium 25% – All other elements 1% • Dust (1%) includes chemical compounds. – methane, ammonia, water, monoxides • Atoms are widely spaced, about 1 atom per cm3, a nearly perfect vacuum. – 1019 atoms/cm3 in air • The temperature is cold, less than 100 K. • Voyager I reached the ISM in 2012. Molecular Clouds • The small mass of atoms creates very weak gravity. – Pull atoms and molecules together • Concentrations equal to 1 million solar masses can form giant molecular clouds over 100 ly across. Diffuse Nebulae • Clouds of gas do not naturally emit light. – Light blocked beyond • The Coal Sack is a dark nebula. • Some nebulae reflect the light of nearby stars. – H I region • The Pleiades are in a reflection nebula. Emission Nebulae • Gas clouds can be heated by nearby stars. – Emits own light – H II region • Like a star the spectrum can be analyzed. – chemical composition – Temperature and density – velocity (by Doppler shift) • The Orion Nebula is an emission nebula. Star Formation • A cool (10 K) nebula can be compressed by shock waves. – Shock waves from new stars and exploding stars. exploding star shock waves nebula with areas of higher density Protostars • Local concentrations in a nebula can be compressed by gravity. – Keeps together at low temperature – Contracts to form centers and radiates energy • These are protostars, called T Tauri stars (G, K, M). Birth of the Sun • Gravity continues to pull the gas together. -20 -15 Abs. Magnitude -10 -5 0 1 M • Hydrogen fusion begins at 5 million K. 5 10 15 20 O B A F G K M Spectral Type • At this point the star has reached the main sequence. Birth of Other Stars • Large masses become brighter, hotter stars. -20 -15 Abs. Magnitude -10 -5 10 M 0 3 M 0.5 M 5 10 0.02 M 15 20 O B A F G K M Spectral Type – Fusion starts sooner, about 100,000 years • Small masses become dimmer, cooler stars. – Fusion starts later, up to 100 million years