* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 8: Astronomy
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Discovery of Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Naming of moons wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Galilean moons wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
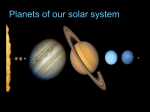
Unit 8: Astronomy A Trip Through the Solar System The Universe A solar system is a star and all the celestial objects that orbit that star. A galaxy is a cluster of billions of stars in a general location in space. The Universe is composed mostly of empty space and hundreds of billions of galaxies. The Milky Way Galaxy A spiral galaxy. The Sun is located on one of the spiral arms. It is believed that a black hole is located in the center of the galaxy. Our Star, the Sun… At the center of the solar system lies the Sun, the solar system’s most massive object. The Sun gets it’s energy by nuclear fusion. The Sun fuses Hydrogen atoms into Helium atoms. The Sun is one of billions of stars in The Milky Way Galaxy. Mercury The closest planet to the Sun Has many impact craters much like the moon Almost no atmosphere to speak of No moons Venus Very similar to Earth in terms of size, density and mass Cannot see the surface of Venus due to thick cloud cover Atmosphere made of 96% carbon dioxide results in very hot temperatures Earth Atmosphere contains free oxygen allowing life to exist Only place where life has been found so far You should know a lot about this planet by now! Mars The last of the terrestrial planets Very thin atmosphere made primarily of carbon dioxide Very cold compared to Earth, and about half the size Reddish appearance from oxidation of minerals such as iron Mars has 2 moons Asteroid Belt Located between Mars and Jupiter are the rocky remains of a Planet that never formed. An asteroid that escapes the belt is called a meteor. A meteor that lands on a planet is called a meteorite. Most meteors burn up in the Earth’s Atmosphere and are called “shooting stars”. Jupiter The first of the Jovian (Jupiterlike) planets Largest planet in the solar system Jupiter’s atmosphere is made of mostly hydrogen and helium (much like a star) The Great Red Spot on Jupiter is a hurricane-type feature about 4 times the diameter of Earth Jupiter has 16 moons Saturn Also a gas giant (Jovian) planet Has spectacular rings made of ice, rocks and dust Radiates more energy than it receives from the Sun due to tremendous pressure in it’s interior Saturn has 18 moons Uranus Uranus is the third Jovian planet Also has rings, but not as prominent as Saturn’s Axis is tilted by 98°, so one pole is always facing the Sun Uranus has 21 moons Neptune The outermost gas giant (Jovian planet) in the Solar system Atmosphere made mostly of hydrogen and helium, but also methane which gives the planet a blue color Strongest winds in the solar system estimated at 2,500 km/hr Neptune has 8 moons Pluto Smallest of the planets with a very eccentric orbit makes “planet” status debatable (recently kicked out). Smaller than our moon Sometimes closer to the Sun than Neptune Has one moon that is more than half it’s size – very unusual Comets Considered part of our solar system because they orbit our Sun. Ice and debris that make a very eccentric orbit around the sun. When a comet is close to the sun its tail ignites and becomes visible. Hailey’s Comet returns into view every 75 years. Comet Orbit Average Densities of the Planets The graph on the right shows the average densities of the planets (Mercury on the left and Pluto on the right). Which four planets are densest? Which four are least dense? Which planet could float in water? 6 5 Average Density 3-D Column 2 3-D Column 3 4 3 2 1 0 M E J U P