* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download oct81
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Exoplanetology wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
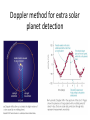
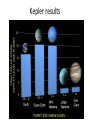
Formation of the Solar System Simulation Terrestrial & Jovian planets Discussion Given the composition of the solar nebula, why do you think all the terrestrial planets have smaller masses than the Jovian planets? 98% hydrogen and helium 1.4% hydrogen compounds – CH4, NH3, H2O 0.4% silicate rocks 0.2% metals Discussion Can the Earth hold hydrogen and helium gas in its atmosphere? How do you know? Discussion Do you think any of the other terrestrial planets hold hydrogen and helium gas? Discussion Why do you think the cores of all the Jovian planets have a mass about 10 times the mass of the Earth? Jovian Planets Once at protoplanet reaches a mass of about 10 times that of the Earth, it can capture large amounts of gas directly from the solar nebular, becoming a Jovian planet. Discussion Why do you think Uranus and Neptune didn’t get as big as Jupiter and Saturn? What about Pluto and the other TNO’s Just the proto-cores of would-be Jovian planets that never got massive enough to hold H and He. Doppler method for extra solar planet detection Discussion What planet characteristics (mass and distance from the star) will be easiest to find with the Doppler method? Explain your reasoning. Extra Solar planets Many extra-solar planets are Jupiter-like planets which lie very close to their star. NASA’s Kepler mission indicates that hot Jupiter’s are not very common. Kepler results Planetary Migration Most likely these hot Jupiters formed beyond the frost-line, but due to close encounters with other protoplanets lost orbital speed and spiraled in toward the star. The Sun Discussion Why does the Sun shine? Discussion How do you know the Sun is hot? Discussion How do we know the temperature of the Sun? Discussion Why is there less solar intensity at sea level than there is at the top of Earth’s atmosphere? Discussion Where do you think that energy goes? Discussion Why isn’t the Sun a perfect blackbody? Solar Data Radius: Mass: Composition: Mean density: Luminosity: 109 Earth radii 333,000 Earth masses 74% hydrogen 25% helium 1.41 g/cm3 3.86 1026 Watts Discussion How do we know the mass of the Sun? The Sun as a big cosmic light bulb Suppose every human being on Earth turned on 1000, 100-watt light bulbs. With about 6 billion people this would only be 6 1014 watts. We would need 670 billion more Earth’s doing the same thing to equal the energy output of the Sun. Cooling Ember theory Anaxagoras (500 – 428 B.C.E.) believed the Sun was a very hot, glowing rock about the size of Greece. Discussion If the Sun were cooling down over time, how could we tell? Thermal equilibrium The Sun is not measurably heating up or cooling down. No cooling ember At the rate that the Sun is emitting energy, the Sun must have been much hotter just a few hundred years earlier, making life on Earth impossible. The Sun must have an energy source; a way of generating its own heat. Discussion Given the composition of the Sun, why is it unlikely that it could be heated by the burning of wood or coal? Kelvin-Helmoltz contraction As things contract gravitationally, they become hotter. Discussion Why do you think gravitational contraction leads to a temperature increase? Discussion If the Sun is getting its energy from KelvinHelmoltz contraction, how could you prove this? Do you think this is an easy thing to do? Explain. Hydrostatic Equilibrium The Sun is not measurably expanding or contracting